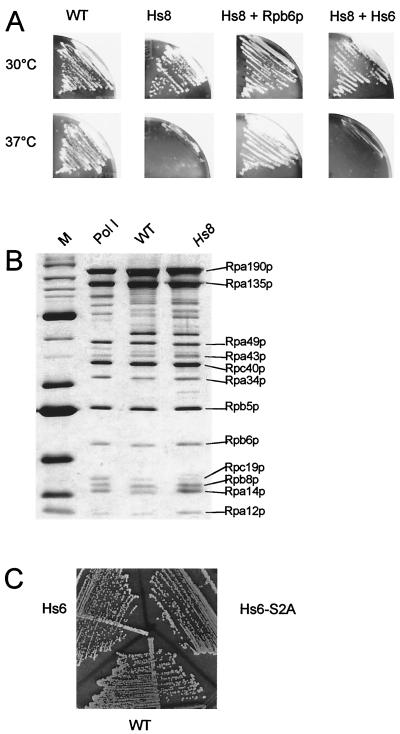
FIG. 2.
Genetic interactions between Rpb6p and Rbp8p. (A) Strains YGVS043 (rpb8-Δ::LYS2 with the yeast RPB8 gene [WT]), YGVS045 (rpb8-Δ::LYS2 with the human Hs8 gene [Hs8]), YJB026 (YGVS045 with a centromeric plasmid expressing the yeast RPB6 gene [Hs8 + Rpb6p]), and YJB027 (YGVS045 with a centromeric plasmid expressing the human Hs6 gene [Hs8 + Hs6]) were streaked on YPD and incubated for 3 days at 37°C. Strain genotypes are listed in Table 1. (B) Five micrograms of a highly purified and catalytically active preparation of Pol I and of two purified preparations from YGVS043 (WT) and YGVS045 (Hs8) strains was separated by SDS–8 to 12% PAGE and silver stained. Individual subunits were identified from their apparent molecular weight, in parallel with standard protein markers (lane M) and a purified Pol I sample (15). (C) Strains JAY444 (rpb6-Δ::LEU2 with the yeast RPB6 gene [WT]), YGVS003 (rpb6-Δ::LEU2 with the human Hs6 gene [Hs6]), YGVS004 (rpb6-Δ::LEU2 with the human Hs6 gene and an S2A mutation [Hs6-S2A]) were streaked on YPD and incubated for 3 days at 30°C, showing the same growth pattern (this observation was made at temperatures ranging from 16°C to 37°C). Strain constructions and genotypes are in Table 1.