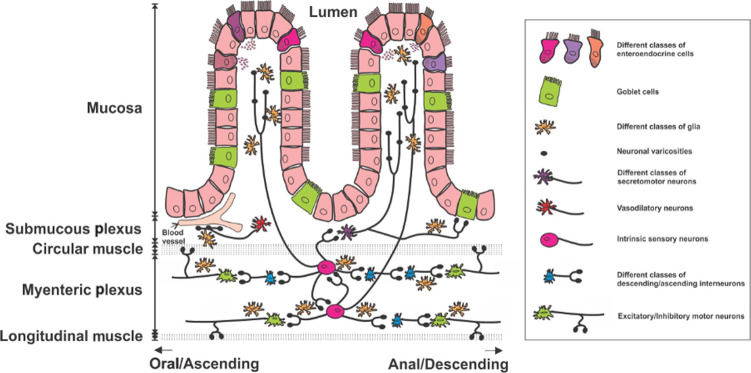
Fig. 1. The structure of the ENS.
The ENS is made up of neurons and glial cells found within layers of the intestinal wall. Neurons of the ENS are grouped into two main plexi, the myenteric plexus and the submucosal plexus. Intrinsic sensory neurons detect mechanical and chemical signals from the lumen and pass information to secretomotor neurons, vasodilator neurons, interneurons and motor neurons. Enteric neurons communicate via neurotransmitter release from the axonal swelling structures known as varicosities. Several types of epithelial cells line the mucosa layer, including different types of enteroendocrine cells and goblet cells, can also interact with enteric neurons and glial cells to control GI physiology. Foong JPP, Hung LY, Poon S, Savidge TC, Bornstein JC. Early life interaction between the microbiota and the enteric nervous system. American Journal of Physiology-Gastrointestinal and Liver Physiology 2020; 319(5): G541–G548.