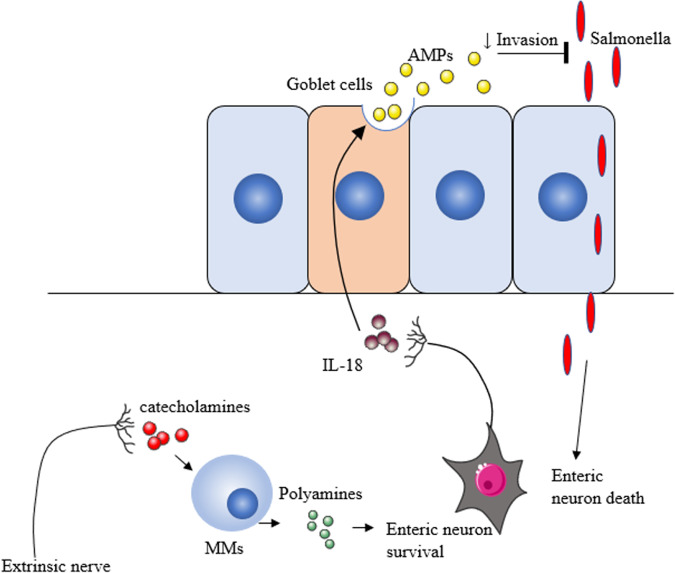
Fig. 3. Neuroimmune interactions in salmonella infection.
Invasion of salmonella causes the death of enteric neurons. However, catecholamines produced by extrinsic nerves induce MM to secrete neuronal protective polyamines, which promotes the survival of enteric neurons. Enteric neurons also release IL-18 which stimulates the production of antimicrobial proteins (AMPs) by goblet cells and reduces invasion of salmonella across the epithelial barrier. Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported (CC BY 3.0).