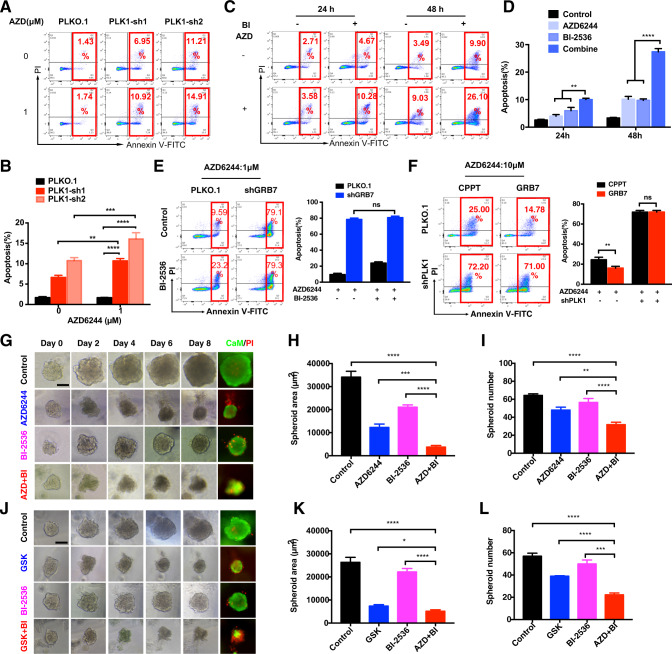
Fig. 6. Combined genetic or pharmacologic inhibition of PLK1 and MEKi treatment promoted apoptosis in KRAS mutant colon cancer cells.
A, B Knockdown of PLK1 by shRNAs induced apoptosis upon AZD6244 treatment in HCT116. B Quantification of (A). Data represented as mean ± SD (n = 3). C, D Apoptosis assay showing that BI-2536 sensitized HCT116 cells to AZD6244. D Quantification of (C). Data represented as mean ± SD (n = 3). E HCT116 cells infected with shRNA targeting GRB7 or vector control, then treated with or without BI-2536 in the presence of 1 μM AZD6244 for 48 h. Data represented as mean ± SD (n = 3). F HCT116 cells infected with vector control, Flag-GRB7, shRNA targeting PLK1, or the combination of both, then treated with 10 μM AZD6244 for 48 h. Apoptosis was detected by annexin V/PI staining. Data represented as mean ± SD (n = 3). G–I Representative phase-contrast and immunofluorescence staining images of HCT116 treated with DMSO, AZD6244, BI-2536, or the combination of both for 8 days in 3D culture system (CaM: green; PI: red). Scale bar, 100 μM. H Quantification of spheroid area. I Quantification of spheroid number. J–L Representative phase-contrast and immunofluorescence staining images of SW480 treated with DMSO, GSK, BI-2536, or the combination of both for 8 days in 3D culture system (CaM: green; PI: red). Scale bar, 100 μM. K Quantification of spheroid area. L Quantification of spheroid number. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, or ****p < 0.0001.