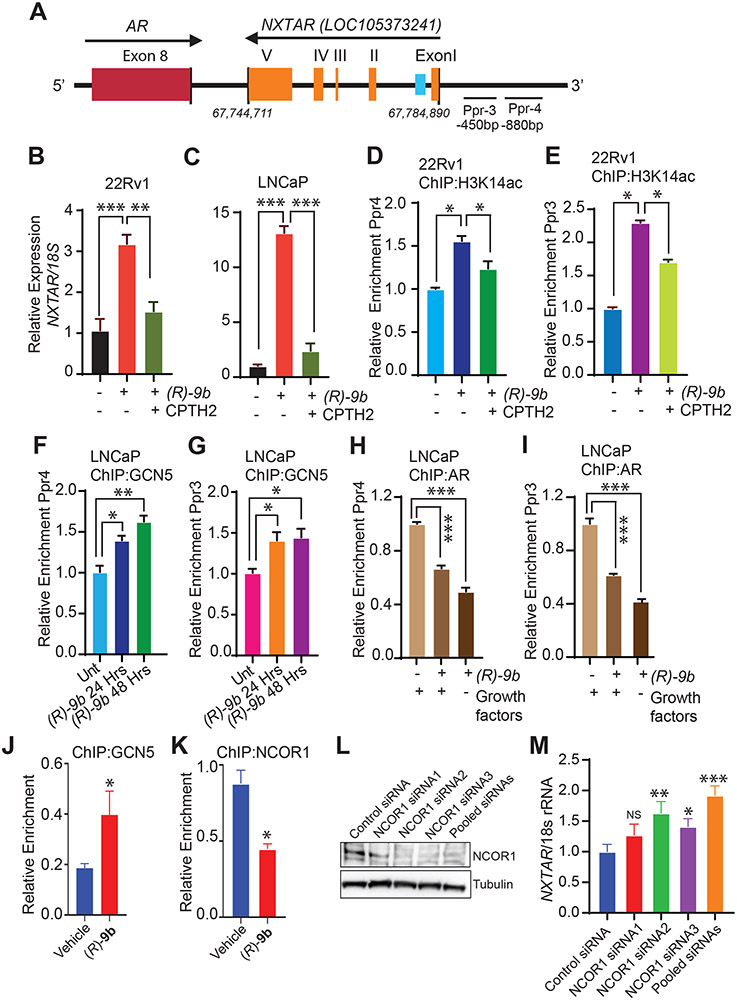
Figure 4: ACK1 inhibition induces NXTAR expression by increasing acetylation of H3K14 at NXTAR promoter.
A, Graphical representation of primers (Ppr3 and Ppr4) upstream of the NXTAR transcription start site. The numbers indicate nucleotide position. B and C, 22Rv1 (B) and LNCaP (C) cells treated with either vehicle or (R)-9b alone or in combination with a GCN5 inhibitor, CPTH2 were processed for total RNA extraction and qRT-PCR was performed with primers for NXTAR and 18S rRNA. D-E, 22Rv1 cells were treated with either vehicle or (R)-9b alone or in combination with CPTH2 and ChIP was performed using H3K14ac antibody or IgG (Supplementary Fig. S9A and B), followed by qPCR using (D) PPr4 and (E) PPr3 primers. F-G, LNCaP cells treated with (R)-9b alone or in combination with CPTH2 were subjected to ChIP using GCN5 antibody or IgG (Supplementary Fig. S9C and D), followed by qPCR using (F) Ppr4 and (G) Ppr3 primers. H-I, LNCaP cells were treated with either (R)-9b alone or in combination with CPTH2 were harvested and processed for ChIP using antibody against AR or IgG (Supplementary Fig. S9E and F), followed by qPCR using (H) PPr4 and (I) PPr3 primers. J, 22Rv1 cells were treated with either vehicle or (R)-9b, subjected to ChIP using GCN5 antibody, followed by qPCR using IRF8 binding site primers. K, VCaP cells were treated with either vehicle or (R)-9b, subjected to ChIP using NCOR1 antibody, followed by qPCR using NXTAR enhancer primers. L, VCaP cells were transfected with control siRNA and three sets of NCOR1 specific siRNAs (1, 2, 3 and pool) and the cell lysate was subjected to immunoblotting. M, RNA isolated processed from these cells was subjected to qRT-PCR using NXTAR and 18S rRNA specific primers. Data are represented as mean ± SEM. *p ≤0.05; ** p<0.01; ***p<0.001, two-tailed Student’s t-test. NS, not significant.