Figure 2. Genome-wide gene expression experiments reveal EGR1 as the main mediator of the early human neutrophil response to S. aureus.
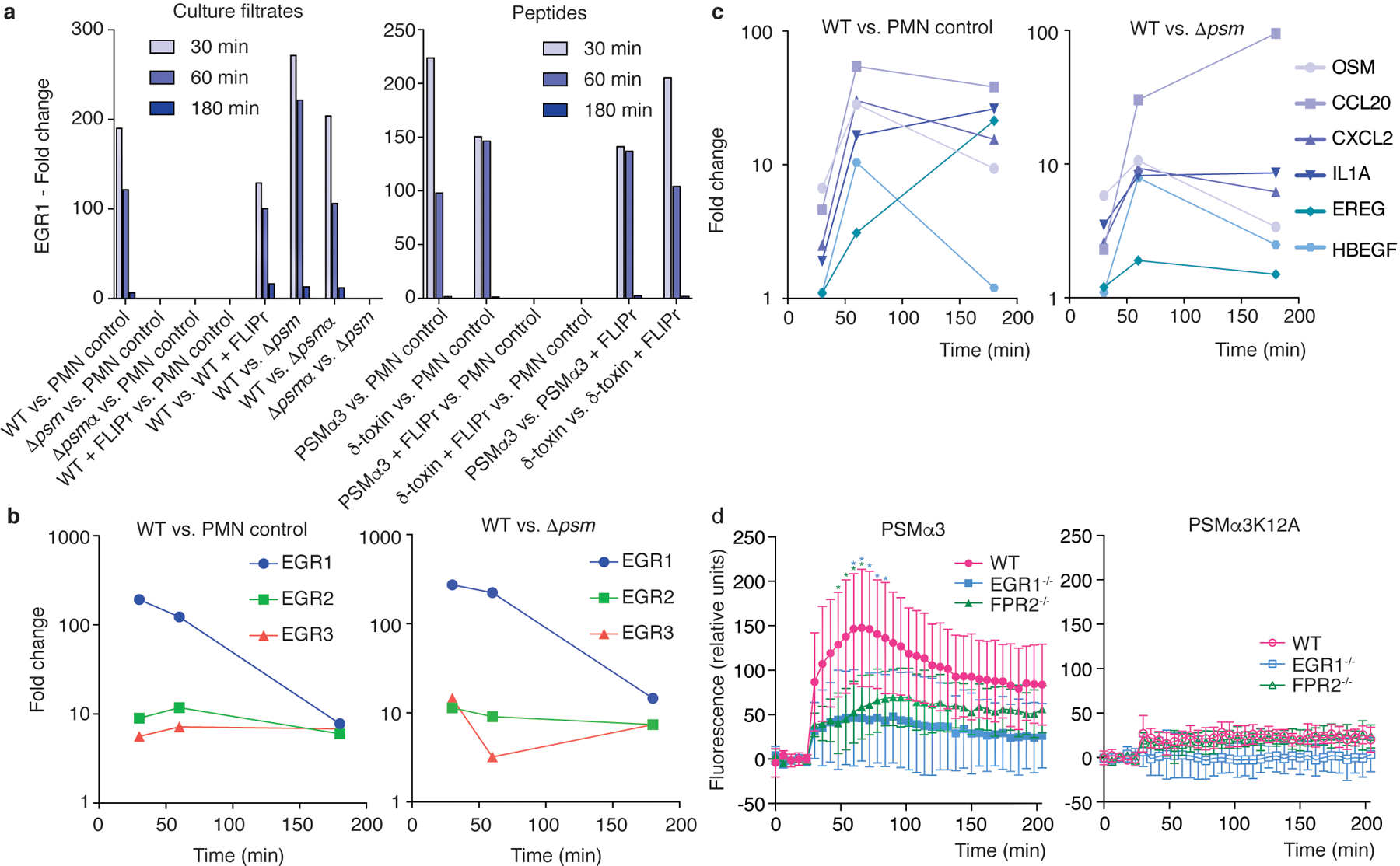
Bacterial culture filtrates (8 h of growth in TSB, at 1: 600 sublytic dilution; see Extended Data Fig. 3) or synthetic PSM peptides (330 nM, sublytic concentration; see Extended Data Fig. 3) were given to 1 × 107 isolated human neutrophils and genome-wide gene expression was determined using microarrays at 30, 60, and 180 min thereafter. a, Differential expression of the transcription factor EGR1 in the indicated comparisons. b, Differential expression of EGR1, EGR2, and EGR3 over time in the indicated comparisons. c, Differential expression of selected cytokine genes over time in the indicated comparisons. See Supplementary Tab. 1 for a list of main genes with strong differential expression (all annotated genes with > factor 10 up-regulation at 30 or 60 min, or > factor 20 at 180 min) in the WT vs. PMN control and WT vs. Δpsm comparisons and GEO (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/query/acc.cgi?acc=GSE103779) for the entire microarray data. d, Stimulation of Ca2+ flux in wild-type (WT), EGR1−/− and FPR2−/− neutrophils by PSMα3 or PSMα3K12A (200 nM). Statistical analysis is by repeated measures 2-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post-tests. Asterisks show statistically significant difference (p<0.05) with the color representing the respective comparison (blue, WT versus EGR1−/−; green, WT versus FPR2−/−). n=6/group. Error bars show the mean ± SD.
