Fig. 7.
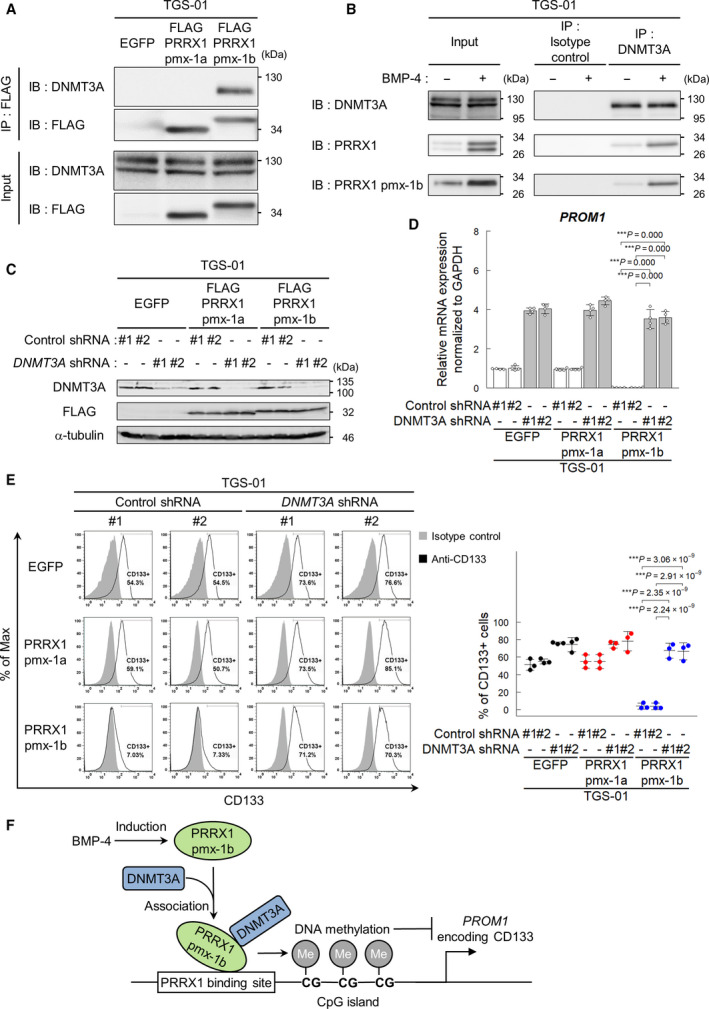
DNMT3A is required for downregulation of CD133 expression by PRRX1 pmx‐1b isoform. (A, B) Immunoblot analysis to examine the physical interaction between DNMT3A and PRRX1. In TGS‐01 cells expressing FLAG‐tagged PRRX1, DNMT3A was co‐immunoprecipitated with FLAG‐tagged PRRX1 pmx‐1b, but not with FLAG‐tagged pmx‐1a (A). In TGS‐01 cells treated for 72 h with or without BMP‐4 (30 ng·mL−1), endogenous PRRX1 pmx‐1b was co‐immunoprecipitated with DNMT3A (B). Representative data of the three independent experiments are shown (A, B). (C–E) DNMT3A shRNA and FLAG‐tagged PRRX1 were transduced into TGS‐01. Immunoblot analysis showing the expression of DNMT3A shRNA and FLAG‐tagged PRRX1 in TGS‐01 cells (C). Expression of PROM1 in TGS‐01 cells expressing DNMT3A shRNA and PRRX1 (n = 4 biological replicates) (D). CD133 expression on cell surface evaluated by flow cytometric analysis in TGS‐01 cells (n = 3 biological replicates) (E). The graphs in panels (D, E) represent mean ± SD of biological replicates. The P‐values were determined by Tukey’s test (D, E). (F) A scheme showing the regulation of CD133 expression by PRRX1 pmx‐1b and DNMT3A regulated by BMP stimulation. Of the two splice isoforms, only the longer isoform of PRRX1, pmx‐1b, induces the differentiation of GICs. Through functional cooperation with DNMT3A, pmx‐1b induces the promoter methylation of the key stem cell marker gene PROM1 by recruitment of DNMT3A and suppresses the CD133‐positive GIC population.
