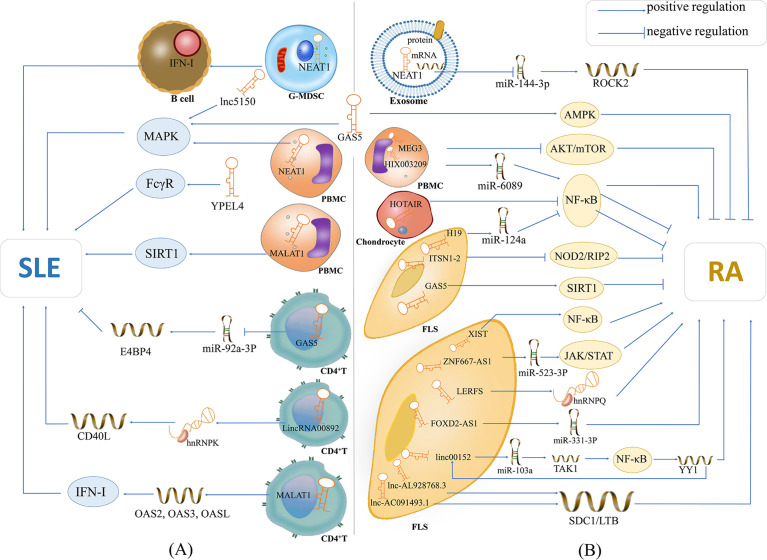
Figure 1.
The potential mechanisms of lncRNAs in SLE and RA. (A) lncRNA NEAT1 is overexpressed in G-MDSCs and induces the promotion of G-MDSCs on IFN-I signaling activation of B cells, contributing to the pathogenesis of SLE; lnc5150 and GAS5 in serum participate in the regulation of the MAPK signaling pathway, and promote the inflammatory response of SLE; lncRNA YPEL4 in serum promotes the onset of SLE through FcγR-mediated phagocytosis; lncRNA NEAT1 in PBMCs affects the expression of inflammatory mediators through activating the MAPK signaling pathway; lncRNA MALAT1 is overexpressed in PBMCs and can modulate the SIRT1 pathway directly, then promote the inflammatory response of SLE; lncRNA GAS5 in CD4+ T cells can upregulate E4BP4 by inhibiting miR-92a-3p and attenuating the self-reactivity of CD4+ T cells, playing a protective role in SLE; LincRNA00892 can activate CD4+ T by targeting hnRNP K and subsequently up-regulating the expression of CD40L, thereby playing a pathogenic role in SLE; lncRNA MALAT1 in CD4+ T cells can participate in type I interferon-mediated SLE by up-regulating OAS2, OAS3 and OASL. (B) lncRNA NEAT1 shuttled by PBMC-derived exosomes plays critical role in the development of RA by acting as a ceRNA for miR144-3p to restrict its function, and thus increase the expression of the miR144-3p-targeted gene ROCK2; lncRNA GAS5 in the serum of patients with RA activates the AMPK pathway; lncRNA MEG3 acts as ceRNA to inhibit inflammation by down-regulating AKT/mTOR signaling pathways; lncRNA HIX003209 in LPS-treated chondrocytes promotes the proliferation and activation of macrophages by modulating the inhibitory effect of the IκBα/NF-κB signaling pathway; lncRNA HOTAIR inhibits the activation of NF-κB in chondrocytes and reduce inflammation of RA; lncRNA-H19 acts as the ceRNA of miR-124a to inhibit the proliferation and invasion of RASF; lncRNA ITSN1-2 inhibits the NOD2/RIP2 signaling pathway and reduces the proliferation and inflammation of RA-FLS; GAS5 in FLS acts as a ceRNA to directly target miR-222-3p, upregulates the expression of Sirt1 and inhibits the proliferation and inflammation of RA; lncRNA XIST can inhibit the proliferation of SFs by promotion of of miR-126-3p/NF-κB pathway, thereby playing a protective role in RA; lncRNA ZNF667-AS1 is overpressed in RA-FLS, which plays a protective role in RA by sponging miR-523-3p and thus inactivation of JAK/STAT signaling pathway; LncRNA LERFS is lowly expressed in RA-FLS and can promote synovial aggression and joint destruction by interacting with hnRNP Q; lncRNA FOXD2-AS1 can promote the proliferation and invasion of RA-FLS through regulating the miR-331-3p/PIAS3 pathway; lncRNA linc00152 is up-regulate in RA-FLS, which can promote TAK1 expression by targeting miR-103a and thus activate the NF-κB pathway; lncRNA AL928768.3 and lnc-AC091493.1 can regulate their target mRNAs (e.g., SDC1, LTB), and thus implicate in the abnormal immune response of RA or promote the proliferation of FLS via multiple pathways in patients with RA. Also, transcription factor YY1 can promote linc00152 expression directly, and thus forming a linc00152/NF-κB feedback loop, which can promote RA-FLS inflammation.