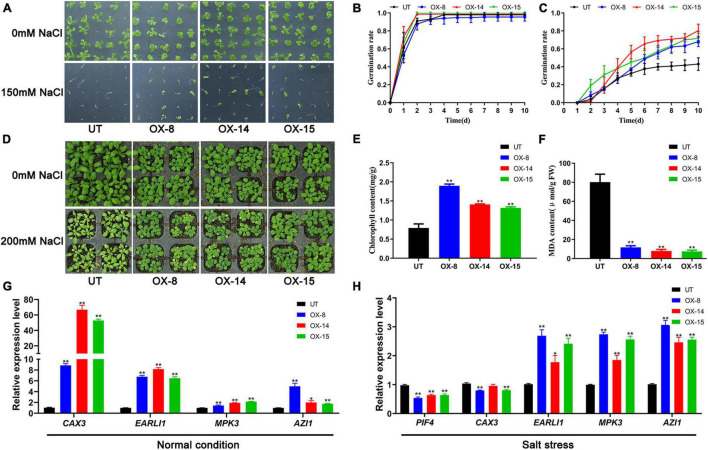
FIGURE 4.
GmMYB133 confers plant tolerance to salt stress in Arabidopsis. (A) Photographs of seed germination for UT plant and three transgenic lines overexpressing GmMYB133 under normal condition and salt stress (150 mM NaCl), which were taken 10 days after culturing under the condition of 16/8 h (light/dark) at 22°C. (B,C) Germination assay of UT and three transgenic lines under normal condition (B) and salt stress (C). The seeds were sowed and cultured on MS solid medium supplied with or without 150 mM NaCl, and the germination rates were monitored for 10 days. (D) Photograph of 30-day-old plants for UT and three transgenic lines under normal condition and salt stress. The 21-day-old plants were exposed to 200 mM NaCl and normal condition for 9 days. (E,F) Quantitative analysis of total chlorophylls (E) and MDA (F) in UT and three transgenic lines under normal condition and salt stress. (G,H) The expression patterns of salt tolerance-associated genes in UT and three transgenic Arabidopsis lines under normal condition (G) and salt stress (H). The genes include AtCAX3, AtEARLI1, AtMPK3, AtAZI1, and AtPIF4. Total RNAs were exacted from 14-day-old transgenic seedlings and UT. Values were normalized against the gene AtACTIN8, and the expression level in UT was set as 1. Error bars in panels (B,C,E–H) indicate SE of three biological and technical replicates, and significant differences are denoted by asterisks: *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01.