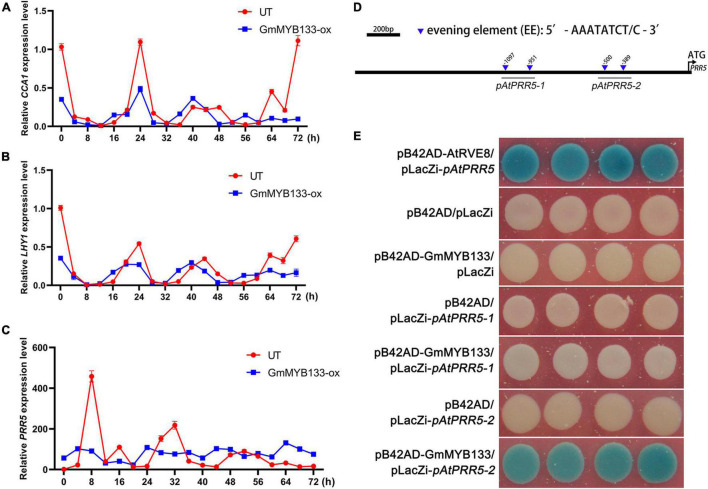
FIGURE 5.
GmMYB133 might affect hypocotyl elongation and salt tolerance directly through regulating the expression of AtPRR5 in Arabidopsis. (A–C) Diurnal expression patterns of three core oscillator genes AtCCA1 (A), AtLHY1 (B), and AtPRR5 (C) in UT plant and the mix of three transgenic lines overexpressing GmMYB133 (OX-8, OX-14, and OX-15). Ten-day-old Arabidopsis seedlings were transferred into the condition of constant light, and the time course was set every 4 h from 0 h until 72 h. Total RNAs were exacted from transgenic seedlings and UT. Values were normalized against the gene AtACTIN8, and the expression level in UT at 0 h was set as 1. Error bars in panel (A–C) indicate the SE of three biological and technical replicates. (D) The schematic diagram of GmMYB133 promoter. The downward triangles indicate the evening element AAATATCT/C, and the number shows the start site of each element. Black lines labeled with pAtPRR5-1 or pAtPRR5-2 represent the examined regions for the Y1H assay. (E) Interaction assay between GmMYB133 and AtPRR5 promoter (pAtPRR5-1 and pAtPRR5-2) using the Y1H approach. Four plasmid combinations were set as negative controls (pB42AD/pLacZi, pB42AD-GmMYB133/pLacZi, pB42AD/pLacZi-pAtPRR5-1, and pB42AD/pLacZi-pAtPRR5-2) and one combination (pB42AD-AtRVE8/placZi-AtPRR5) as positive control.