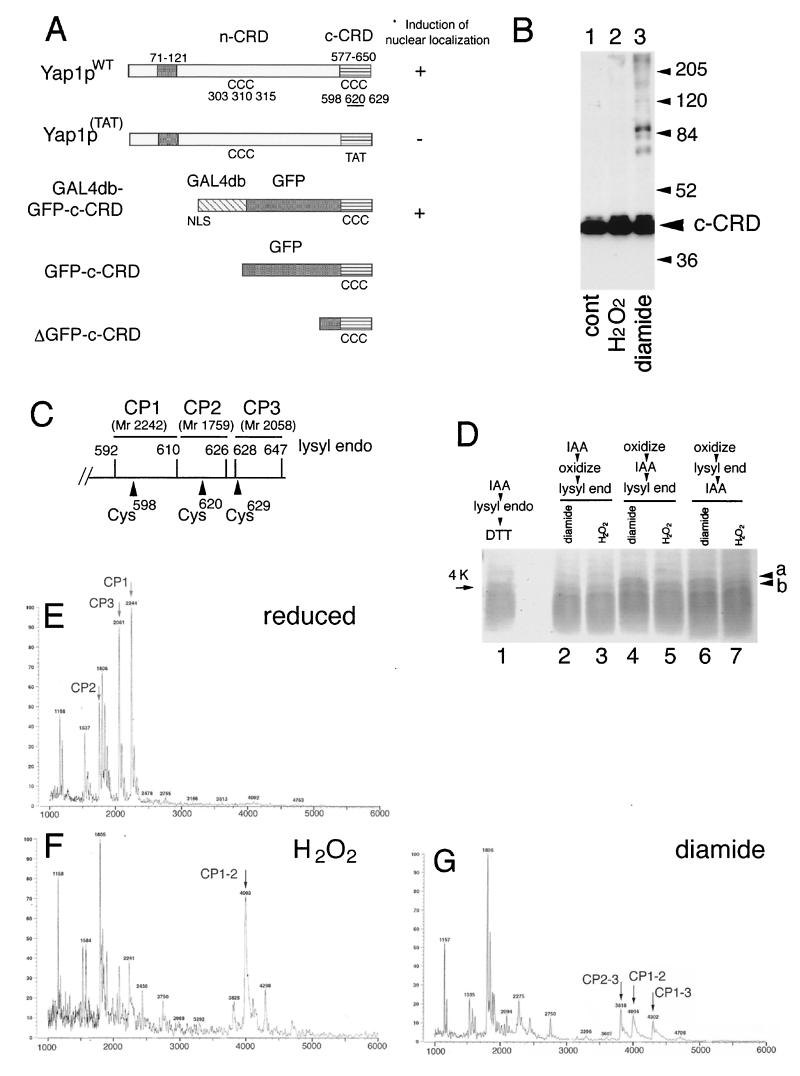
FIG. 1.
Disulfide bond formation in the Yap1p c-CRD. (A) Importance of domains and the cysteine residues of Yap1p for the induction of nuclear localization. Schematic representations of Yap1p (Yap1pWT) and its derivatives are shown. The leucine zipper domain (ZIP; amino acid positions 71 to 121), the n-CRD (position undefined as a domain), and the c-CRD (amino acid positions 577 to 650) are indicated together with the positions of 6 cysteine (C) residues. A mutant with all 3 c-CRD cysteines replaced [Yap1p(TAT), with C598T, C620A, and C629T mutations] and the fusion construct of c-CRD fused to Gal4db and GFP (GAL4db-GFP-c-CRD) is shown. Previously observed (18) phenotypes are indicated. The GFP-c-CRD and ΔGFP-c-CRD used for this study are also shown. (B) TW (yap1) cells carrying pRS HA GFP-c-CRD were untreated (cont) or treated with 0.5 mM H2O2 or 1.5 mM diamide for 30 min. Free thiols were blocked by IAA and were further analyzed for molecular-weight shift by nonreducing SDS-PAGE as described in Materials and Methods. Positions of molecular-weight markers are shown. (C) Lysyl endopeptidase sites (amino acid numbers of lysine residues are indicated) in the c-CRD. The peptides CP1, CP2, and CP3, together with these molecular masses, corresponding to the peptide fragments containing Cys598, Cys620, and Cys629 are shown. (D) Peptide analysis of the c-CRD. The ΔGFP-c-CRD was incubated with 1 mM H2O2 (lanes 3, 5, and 7) or 2 mM diamide (lanes 2, 4, and 6) or no oxidant (lane 1) and was analyzed for lysyl endopeptidase-digested peptide fragments as described in Materials and Methods. IAA treatment was carried out before oxidation (lane 2 and 3) or after oxidation (lanes 4 and 5) or after the peptidase digestion (lanes 6 and 7). (E to G) MALDI-TOF spectra for reduced (E), 1 mM H2O2-treated (F), and 2 mM diamide-treated (G) GFP-c-CRD after lysyl endopeptidase digestion. The peptide peaks CP1, CP2, and CP3 are shown (E). The peaks corresponding to CP1 linked to CP2 (CP1–2) (F and G), CP1 linked to CP3 (CP1–3) (G), and CP2 linked to CP3 (CP2–3) (G) are indicated.