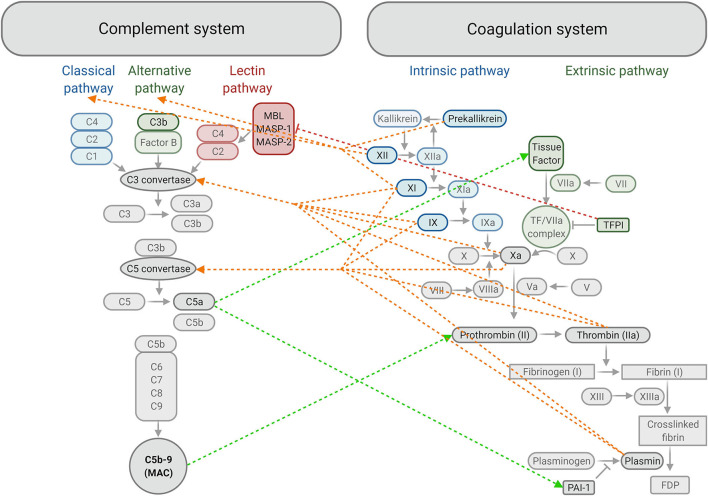
Figure 3.
Summary of crosstalk between components of the complement and coagulation systems. The classical, alternative and lectin activating pathways of complement produce C3 convertase, which allows for downstream activation of C3, C5 and formation of the membrane attack complex (MAC) or C5b-9. Activation of Factor IX in the intrinsic pathway and formation of the tissue factor/FVIIa complex in the extrinsic pathway converge at the common coagulation pathway by activating FX. This allows for the formation of a fibrin clot downstream, strengthening the initial platelet plug, which is later degraded into fibrin degradation products (FDP) by plasmin. Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 (PAI-1) inhibits the formation of plasmin and tissue factor pathway inhibitor (TFPI) inhibits formation of the tissue factor / FVIIa complex. ←-- activation of the complement system by the coagulation system; -- → activation of the coagulation system by the complement system; |– – – inhibition of the complement system by the coagulation system. MBL, Mannose-binding lectin; MASP, Mannose-binding lectin-associated serine protease (created with BioRender.com).