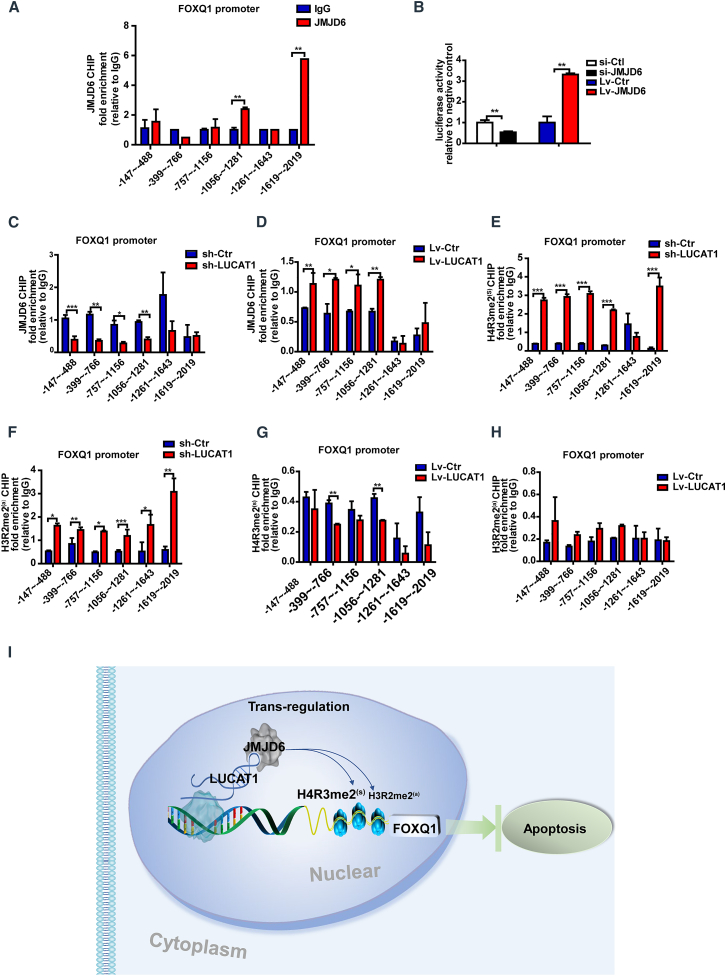
Figure 8.
LUCAT1 regulates FOXQ1 through JMJD6-mediated demethylation of H4R3me2(s) and H3R2me2(a) at the FOXQ1 promoter
(A) ChIP assays were performed with an anti-JMJD6 antibody. IgG was used as the control. Fold enrichment of the indicated regions of the FOXQ1 promoter was examined through qPCR (n = 3). (B) Luciferase assays were used to measure the trigger of JMJD6 at the FOXQ1 promoter (n = 3). (C and D) ChIP-qPCR assays were performed with an anti-JMJD6 antibody and revealed the enrichment of the indicated regions at the FOXQ1 promoter in the LUCAT1-knockdown or -overexpression MSCs compared with the control (n = 3). (E and F) The ChIP-qPCR assay with the anti-H4R3me2(s) and anti-H3R2me2(a) antibodies indicated region enrichment of the FOXQ1 promoter in the LUCAT1-knockdown MSCs compared with the control (n = 3). (G and H) The ChIP-qPCR assay with the anti-H4R3me2(s) and anti-H3R2me2(a) antibodies indicated enrichment of the FOXQ1 promoter in the LUCAT1-overexpressing MSCs compared with the control (n = 3). (I) A schematic illustration of the overall process. Data are presented as the mean ± SEM. ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001.