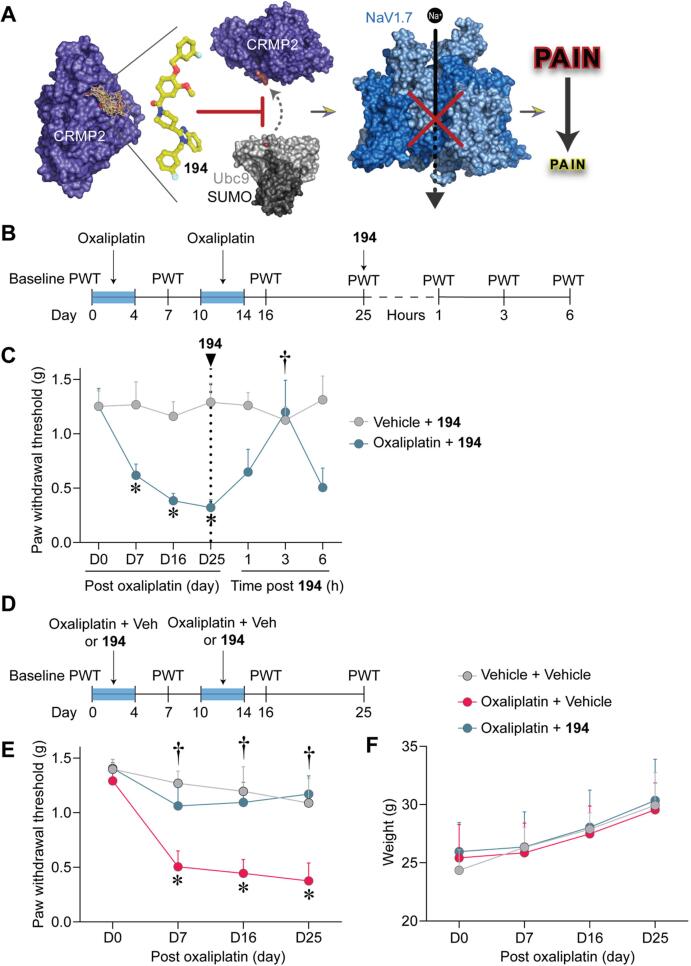
Fig. 1.
194 reduces and prevents the development of mechanical allodynia in male CD-1 mice with oxaliplatin induced peripheral neuropathy. (A) Compound 194 discovery and validation. 194 was designed using the structure–activity relationships of compounds obtained from a virtual screen against a pocket encompassing the SUMOylation target on CRMP2 (PDB 2GSE (Stenmark et al., 2007)). 194 effectively blocks SUMOylation of CRMP2 by the E2 SUMO-conjugating enzyme Ubc9 (PDB 5D2M (Cappadocia et al., 2015)) to reduce cell-surface trafficking of NaV1.7 (PDB 6J8H (Shen et al., 2019)). This results in dramatically reduced sodium currents and amelioration of pain in animal models. Graphic generated with BioRender. (B) Experimental design for behavioral assessment of oral administration of 194 on reversal of oxaliplatin induced CIPN. Baseline paw withdrawal threshold (PWT, in grams) was established at Day 0, followed by induction of CIPN with administration of oxaliplatin between Day 0–4 and Day 10–14 as indicated by the blue box. Mechanical allodynia was evaluated by measuring PWTs at regular intervals as indicated in the timeline. On day 25, mice were orally administered 194 and paw withdrawal thresholds were tested over six hours as indicated. (C) Mice treated with Vehicle and 194 displayed stable PWTs over the experimental time course (gray). Those treated with oxaliplatin developed robust mechanical allodynia that peaked at Day 25 (blue). Treatment with 194 completely reversed the oxaliplatin induced mechanical allodynia to vehicle treated levels 3 h following oral administration. Data are mean ± SD; Two-Way ANOVA with Bonferroni’s multiple comparison *p < 0.05 vs D0; †p < 0.05 vs D25; Oxaliplatin + 194n = 4; Vehicle + 194n = 5. (D) Experimental outline of prevention experiments performed in male CD-1 mice. Baseline PWTs was first established at Day 0, followed by treatment with Vehicle + Vehicle, Oxaliplatin + Vehicle, or Oxaliplatin + 194. PWTs were then assessed at regular intervals as indicated. Blue boxes indicate periods of treatment with oxaliplatin. (E) Mice treated with Vehicle + Vehicle had stable PWTs across the experimental time course (gray). Treatment with Oxaliplatin + Vehicle demonstrated robust mechanical allodynia in male mice (pink). Treatment with Oxaliplatin + 194 prevented the development of mechanical allodynia in these mice (blue). (F) Evaluation of the body weight of mice across the experimental period revealed no significant differences between groups of animals. Data are mean ± SD; Two-Way ANOVA with Bonferroni’s multiple comparison †p < 0.05 vs Oxaliplatin + Vehicle; *p < 0.05 vs D0; Vehicle + Vehicle n = 4; Oxaliplatin n = 5 per group. Experimenters were blinded to the treatment conditions. (For interpretation of the references to colour in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article.)