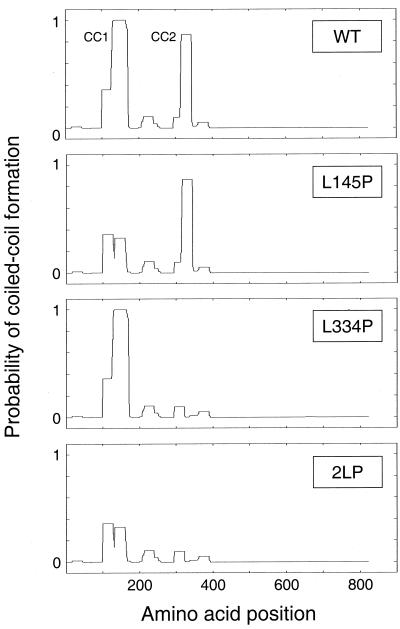
FIG. 1.
Identification of Fes N-terminal residues essential for coiled-coil formation. Wild-type and mutant forms of the 822-amino-acid Fes sequence were analyzed using the COILS algorithm. The probability of each residue contributing to coiled-coil formation is plotted as a function of its position within the overall sequence. The mutant proteins include one with a proline substitution for Leu 145 in the CC1 domain (L145P) protein, one with a proline substitution for Leu 334 in the CC2 domain (L334P protein), and a double mutant protein with both substitutions (2LP). For this analysis, a 28-residue sliding window was used along with the MTIDK matrix. For additional details, see http://www.ch.embnet.org/software/COILS_form.html. WT, wild type.