FIG. 2.
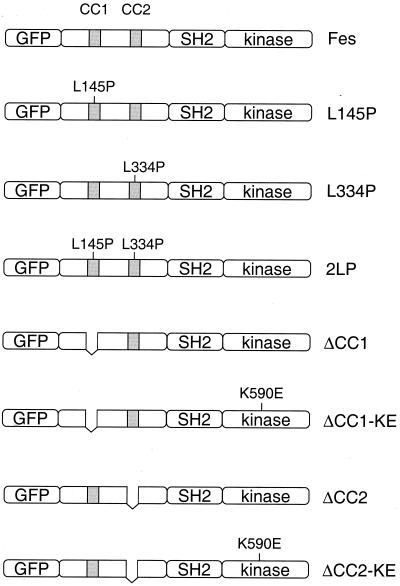
GFP-Fes constructs used in this study. The structure of the wild-type GFP-Fes fusion protein is shown at the top and includes a unique N-terminal region, an SH2 domain, and a C-terminal kinase domain. The locations of the two coiled-coil homology regions are indicated as the shaded boxes (CC1 and CC2). Mutant proteins include one with a proline substitution for Leu 145 in the first coiled-coil domain (L145P), one with a proline substitution for Leu 334 in the CC2 domain (L334P), and the corresponding double mutant protein with both substitutions (2LP). We also constructed GFP fusion proteins of the ΔCC1 and ΔCC2 deletion mutant proteins and the corresponding kinase-inactive forms of these proteins (ΔCC1-KE, ΔCC2-KE). All constructs have a C-terminal FLAG epitope tag (not shown).