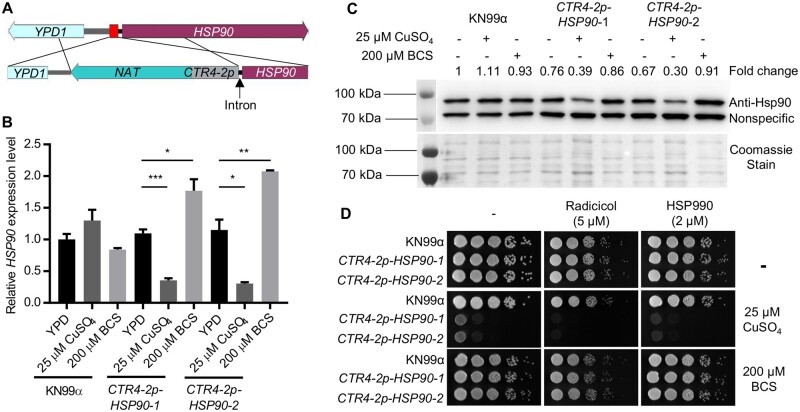
Figure 1.
Generation and characterization of a regulatable expression system for C. neoformans HSP90. (A) Schematic diagram showing the engineering of the CTR4-2p-HSP90 strain. The red box between HSP90 and YPD1 indicates the targeted sequence to be replaced with the NAT-CTR4-2p cassette. (B,C) Wild-type KN99α and two CTR4-2p-HSP90 colonies from a single transformation were grown in liquid YPD medium alone or with CuSO4 or BCS at 37°C overnight. In the morning, strains were sub-cultured in the same liquid media and grown at 37°C for 5 h. Cells were harvested to examine (B) HSP90 expression levels by RT-PCR and (C) Hsp90 protein levels by western blot. (B) Relative level of expression for HSP90 was normalized to GPD1. Expression was normalized to wild type in YPD alone. Error bars represent standard deviation of the mean for technical triplicates. *P ≤ 0.05, **P ≤ 0.01, and ***P ≤ 0.001. (C) Hsp90 protein levels were normalized to nonspecific protein bands recognized by the anti-Hsp90 antibody and set relative to wild-type cells grown in YPD alone. Fold changes of Hsp90 levels are listed above the western blot image and Coomassie stain of the membrane confirming equal loading is shown below, which matches the pattern observed with the nonspecific band. (D) Wild-type and mutant cells from overnight cultures were 10-fold serially diluted and spotted on YPD agar or YPD agar supplemented with CuSO4 or BCS with or without Hsp90 inhibitors. Agar plates were incubated at 37°C and imaged after 2 days.