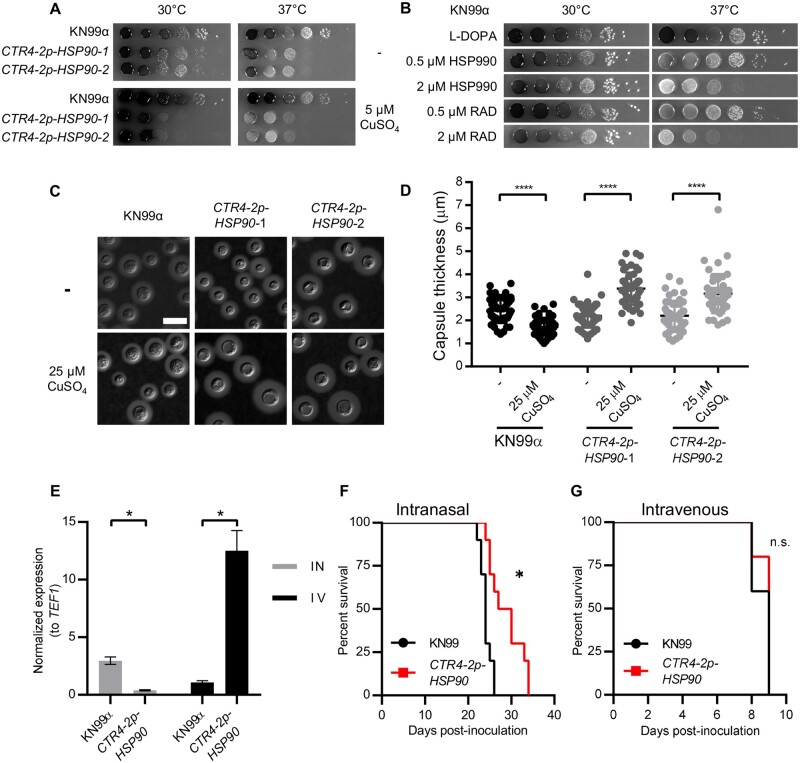
Figure 4.
Hsp90 modulates melanin and capsule production, and depletion of HSP90 attenuates virulence in a pulmonary model of cryptococcal infection. (A) Wild-type and CTR4-2p-HSP90 cells were 10-fold serially diluted and spotted on L-DOPA agar medium with or without CuSO4. (B) Wild-type cells were 10-fold serially diluted and spotted on L-DOPA agar medium with or without Hsp90 inhibitors at the concentrations indicated. Agar plates were incubated at 30°C or 37°C and imaged after 2 days. (C) Representative images of India ink-stained wild-type and CTR4-2p-HSP90 strains show capsule production. Cells were grown in 10% Sabouraud media in 50 mM HEPES (pH7.3) with or without CuSO4 at 30°C for 48 h. Scale bar represents 10 µm. (D) Capsule thickness was measured (N = 50) for samples shown in A. **** P ≤ 0.0001. (E) Lungs were harvested from intranasally (IN, gray bars) inoculated mice and brains from intravenously (IV, black bars) inoculated mice (n = 3 per group). For each sample, relative gene expression levels were measured by qRT-PCR and expression levels for HSP90 normalized to the expression levels of the constitutively expressed gene TEF1. Results were then normalized to the HSP90 expression level determined for wild-type KN99α in brains of intravenously inoculated mice. * P ≤ 0.05. (F,G) A/J mice were inoculated intranasally (F) or intravenously by tail vein injection (G) with the wild-type or CTR4-2p-HSP90 strain (n = 10 mice per group). Mice were monitored for disease progression. *P = 0.0013, n.s. = not significant.