Figure 1. Study design.
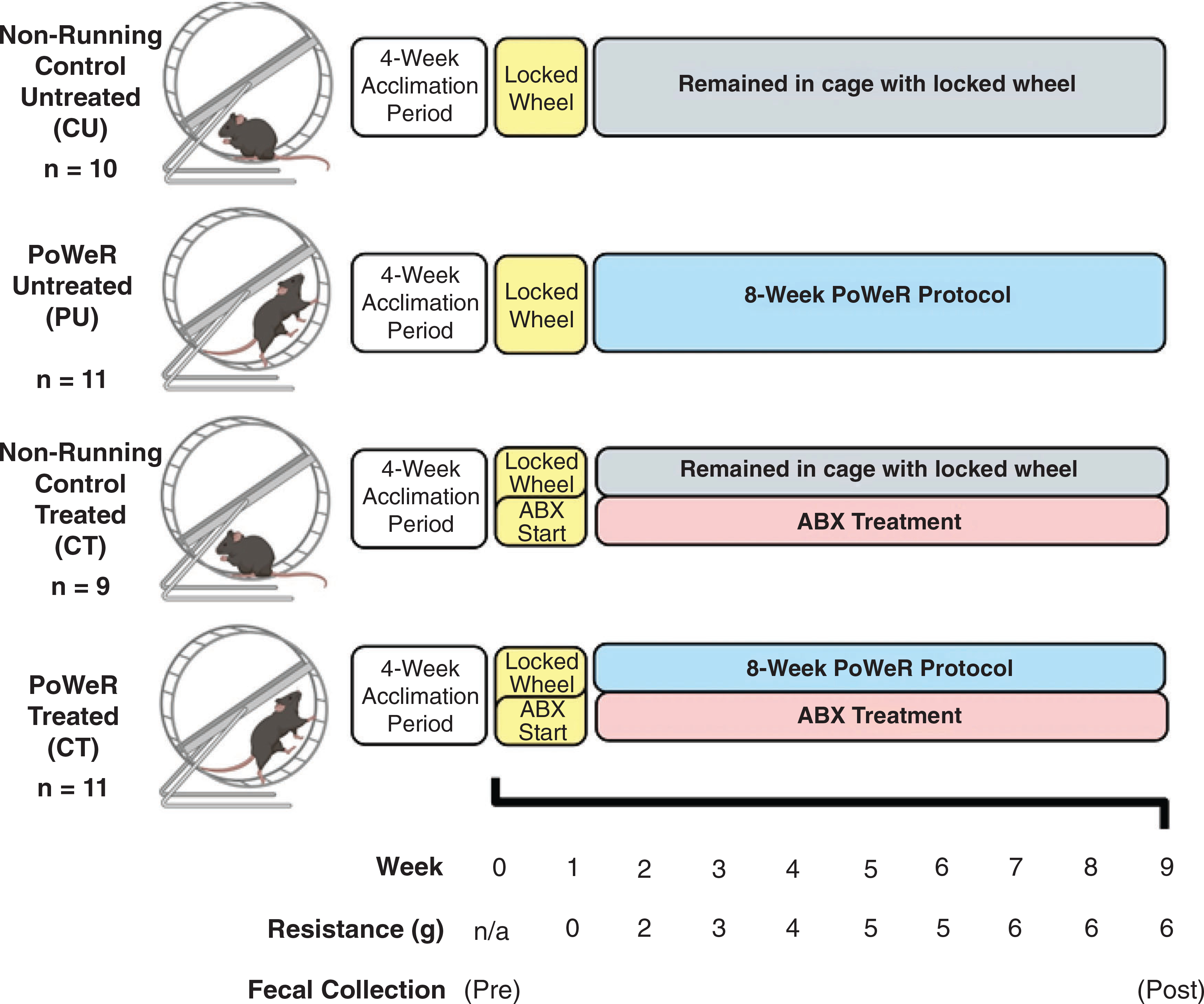
Animals were co-housed in groups of four to five for 4 weeks in order to allow for acclimation to the animal facility at the University of Kentucky. Upon the completion of the acclimation period, mice were randomly split into four different groups and singly housed in running wheel cages. Immediately after randomization into study groups, the first faecal samples were collected (pre), prior to antibiotic administration. During the first week of being singly housed, all wheels were locked, and the antibiotic treatment began. One week after, the wheels were unlocked for those mice in the PoWeR groups, initiating the acclimation week. After the first week of acclimation with an unloaded wheel, 2 g was placed on one side of the running wheel to add resistance Each week thereafter, an additional 1 g was added to the wheel until the load reached a total of 6 g for the final 3 weeks of training. A final faecal sample was collected roughly 48 h prior to euthanasia. After completion of 8 weeks of PoWeR training, mice were euthanized, and tissues were collected for analysis. Image created with BioRender.
