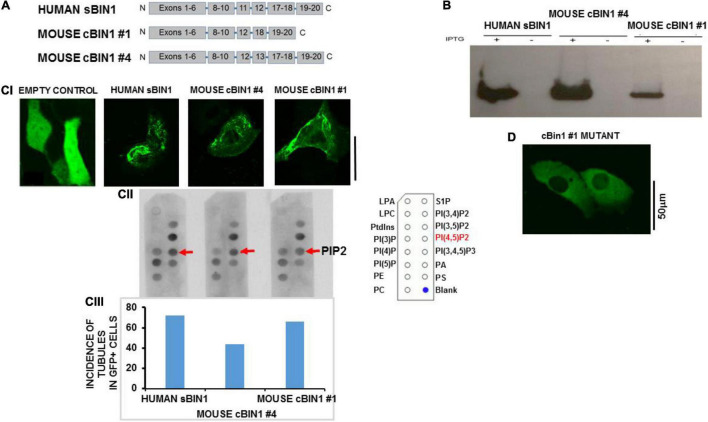
FIGURE 3.
In vitro model of HL1 cells shows tubules after BIN1 overexpression. (A) Gene organization for two splice variants of mouse cardiac muscle BIN1 as well as human skeletal muscle BIN1. (B) The expression of BIN1 proteins induced by isopropyl-b-D-thiogalactoside (IPTG) in bacteria. (C) The interaction between purified Bin1 and PIP2. (CI) Tubule formation in Hl-1 cells 48 h after overexpression with each of the Bin1 constructs. The inset shows that no tubules formed in the overexpression of empty vector. (CII) PIP Strip assays were performed using BIN1 antibody. Representative results from 3 separate experiment are shown and all PIP strip results were confirmed in 1–2 additional strips for each protein. The template describing location of dots for all phospholipids is shown in Supplementary Figure 3. (CIII) Incidence of tubule formation induced by over expressed BIN1 in HL1 cells for each construct. No tubules were formed in cells with empty vector. (N = 48 cells/3 cultures for each including empty vector). (D) Example of an HL-1 cell over-expressing a construct with triple mutations of Lys164Glu/Lys165Glu/Lys166Glu in a loop segment of the N-BAR coiled-coil domain completely abolished tubule formation. No tubulation was found in any GFP-positive cells (N = 36 cells/3 cultures). Note that the vector contains a GFP tag so Bin1 can be easily visualized. Pixel size was 0.11 μm/pixel and all images were obtained with the pinhole adjusted to Airey units = 1.