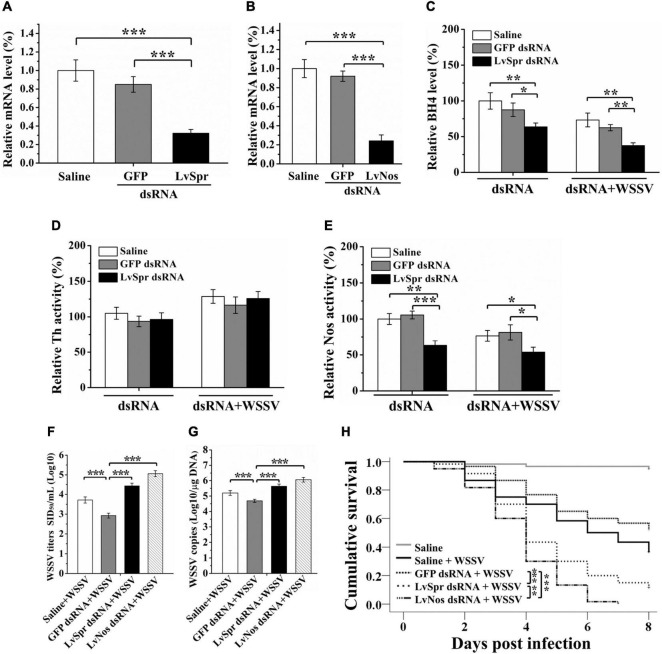
FIGURE 4.
Regulation of BH4 production and BH4 dependent enzyme by LvSpr during WSSV infection. (A,B) qRT-PCR analysis of the RNA interference efficiency of LvSpr (A) and LvNos (B). Shrimp were injected with LvSpr dsRNA, LvNos dsRNA, GFP dsRNA (negative control), and saline (blank control) twice in a 48 h interval. Hemolymph was collected at 48 h after the second dsRNA injection. (C–E) BH4 (C) level and the enzymatic activity of Th (D) and Nos (E) in the HLS of LvSpr knockdown shrimp. The dsRNAs were injected into shrimps twice in a 48 h interval. HLS was prepared to measure the BH4 level and enzymatic activity 48 h after the second injection of dsRNA (left panel) or 48 h after the second injection of dsRNA and WSSV virions (right panel). (F,G) WSSV load (F) and infection titer (G) in the LvSpr, LvNos, and GFP silenced shrimp as well assaline-injected shrimp infected with WSSV. (H) Kaplan-Meier curves showing survival of LvSpr, LvNos, and GFP-silenced and saline-injected shrimp following infection with WSSV. Differences in survival levels between the experimental and control groups were analyzed by Kaplan–Meier log-rank χ2 tests (asterisks indicate significant differences *p < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.001).