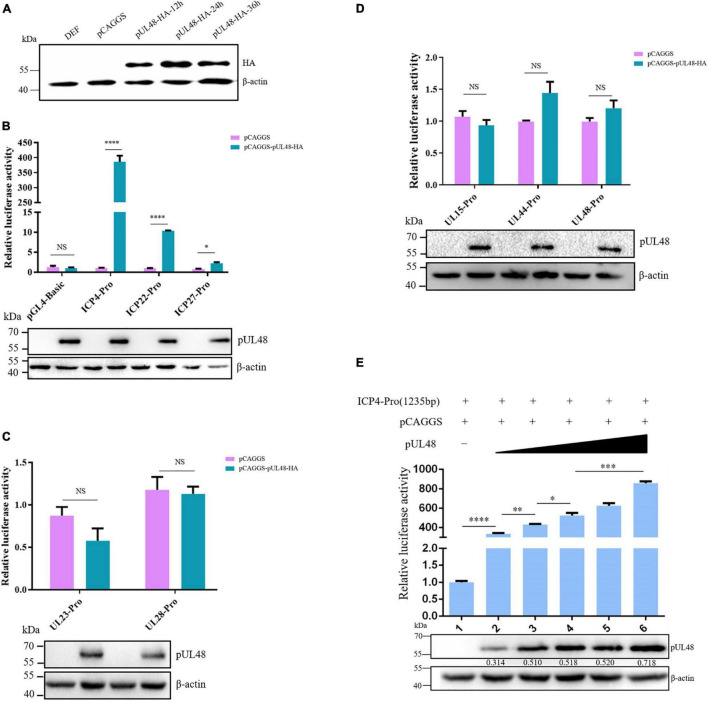
FIGURE 1.
Regulation of pUL48 on duck plague virus (DPV) gene promoters of different types. (A) Expression of pCAGGS-pUL48-HA in DEF. pCAGGS and pCAGGS-pUL48-HA were transfected into DEF, respectively, and cell protein samples were collected at 12, 24, and 36 h for Western blot. (B) The regulation of pUL48 on the IE gene promoter of DPV. (C) The regulation of pUL48 on DPV early gene promoters. (D) The regulation of pUL48 on DPV late gene promoter. (E) Dose-dependent activation of pUL48 on ICP4-Pro (1,235 bp). pGL4-basic, ICP4-Pro-Luc, ICP22-Pro-Luc, ICP27-Pro-Luc, UL23-Pro-Luc, UL28-Pro-Luc, UL15-Pro-Luc, UL44-Pro-Luc, and UL48-Pro-Luc were cotransfected into DEF with pCAGGS, pCAGGS-pUL48-HA, and pRL-TK/0.05, 0.1, 0.2, 0.3, and 0.4 μg pCAGGS-pUL48-HA were cotransfected into DEF with pCAGGS, ICP4-Pro (1,235 bp)-Luc and pRL-TK. Except for the reference plasmid pRL-TK, the transfection ratio of other plasmids was 1:1:1, and the transfection quantity of pRL-TK was 1/20 of the double luciferase plasmids; pCAGGS was a blank group. Cell samples were collected 24 h after transfection. The activity of each promoter was detected by a dual-luciferase reporting system. The corresponding concentration of pCAGGS-pUL48-HA was transfected into DEF. At 24 h after transfection, cell protein samples were collected for Western blot analysis. Student’s t-test was used to analyze the differences of the two groups. The significance was as follows: NS showed no difference, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001.