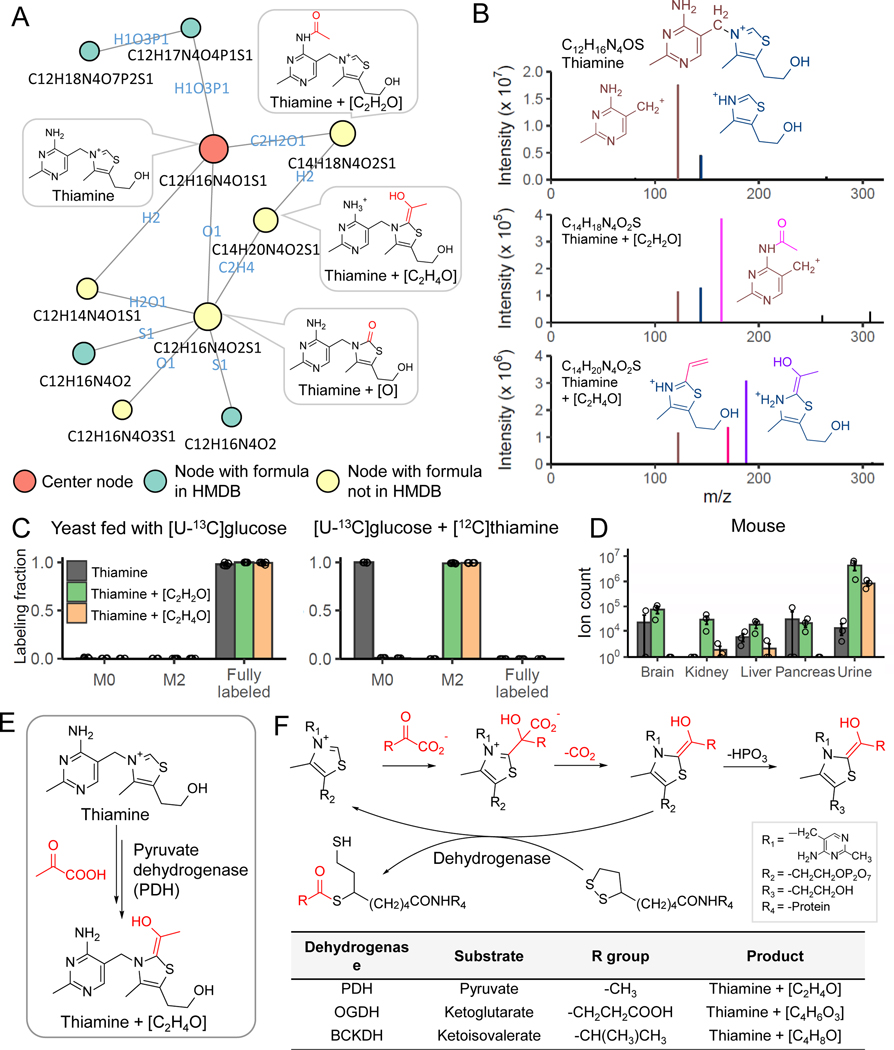
Figure 3. NetID reveals thiamine-derived metabolites in yeast.
(A) Subnetwork surrounding thiamine. Nodes, connections, and formulae are direct output of NetID. Boxes with structures were manually added. (B) MS2 spectra of thiamine, thiamine+C2H2O, and thiamine+C2H4O, with proposed structures of the major fragments. (C) Labeling fraction of thiamine and its derivatives, in [U-13C]glucose with and without unlabeled thiamine in the medium (n = 5). (D) The thiamine derivatives are also found in mouse tissues and urine (n=3). (E) Proposed mechanism for formation of thiamine+C2H4O. Pyruvate dehydrogenase (PDH) decarboxylates pyruvate, and adds the resulting [C2H4O] unit (in red) to thiamine. (F) The same enzymatic mechanism occurs in oxoglutarate dehydrogenase (OGDH) and branched-chain α-ketoacid dehydrogenase complex (BCKDC), and generates thiamine+C4H6O3 and thiamine+C4H8O respectively. Bar represents mean values and error bar indicates s.d. in (C) and s.e. in (D).