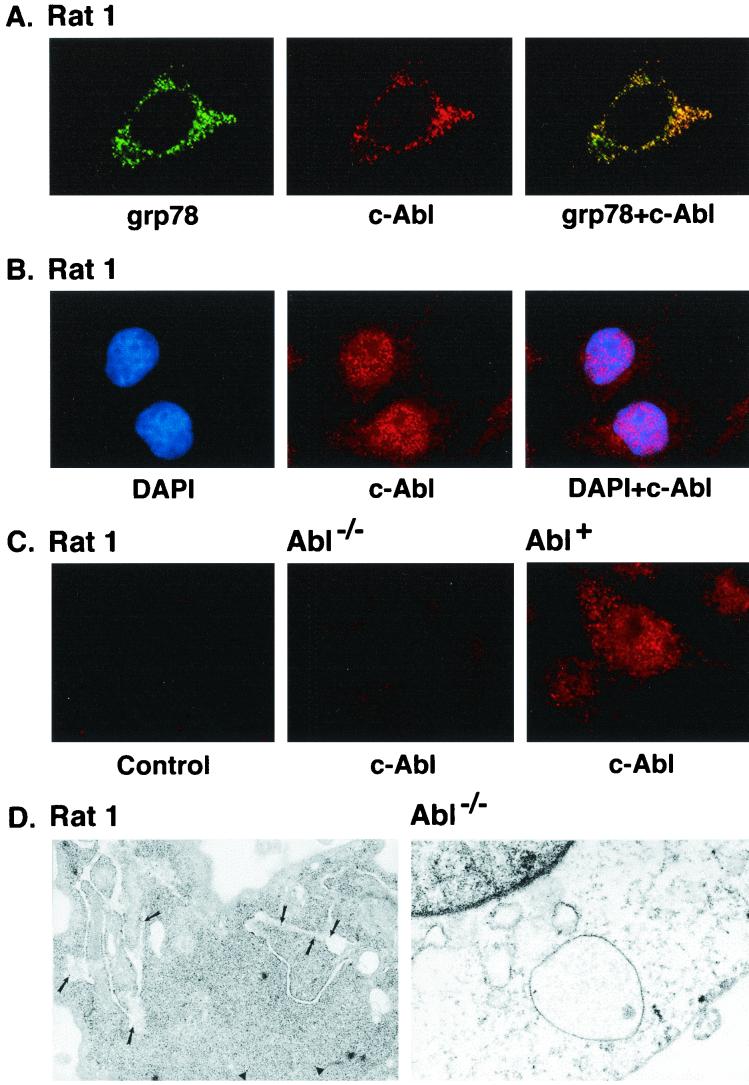
FIG. 1.
(A) Colocalization of c-Abl and ER-associated proteins. Rat1 cells grown on poly-d-lysine-coated coverslips were fixed, permeabilized, and blocked in medium containing serum. Rat1 cells were subjected to immunofluorescence staining with goat anti-grp78 antibody and rabbit anti-c-Abl. The green signals for grp78 were obtained with fluorescein isothiocyanate-conjugated donkey anti-goat IgG (left). The red signal (c-Abl) was obtained with CY-3-conjugated donkey anti-rabbit IgG secondary antibody (middle). Overlay resulted in yellow signals indicative of colocalization (right). The digital confocal image was set for the ER. (B) Rat1 cells were incubated with DAPI (left, blue signal) and rabbit anti-c-Abl. The red signal for c-Abl was obtained with the CY-3-conjugated donkey anti-rabbit IgG (middle). The overlay demonstrates localization of c-Abl in the nucleus (right). The confocal image was set for the nucleus. (C) Rat1 cells were incubated with CY-3-conjugated donkey anti-rabbit IgG (no anti-c-Abl; left). Abl−/− (middle) and Abl+ (right) cells were incubated with anti-c-Abl and CY-3-conjugated donkey anti-rabbit IgG. The confocal image was set for the nucleus and cytoplasm. (D) Rat1 (left) and Abl−/− (right) cells were subjected to immunogold labeling with anti-c-Abl. Gold particles were counted in nine Rat1 cells. The average number of gold particles per cell was 29 ± 14 (mean ± standard deviation). The percentages of total particles in the following subcellular fractions were 57% ± 14% (nucleus), 12% ± 8% (ER), 2% ± 4% (mitochondria), and 29% ± 9% (cytoplasm). Magnification, ×30,000.