FIG. 5.
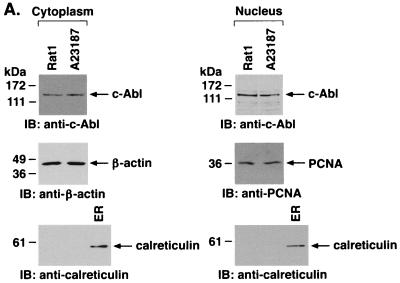
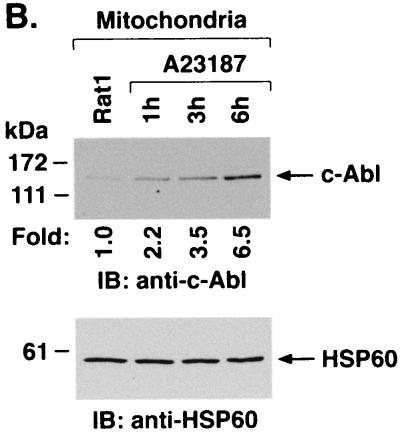
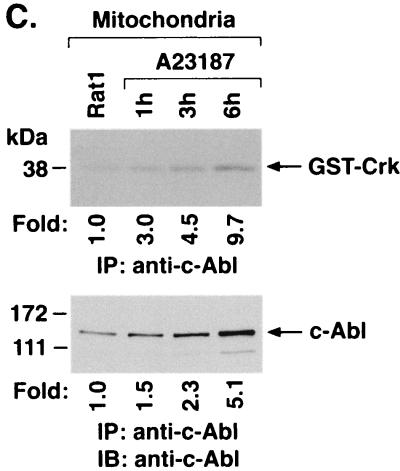
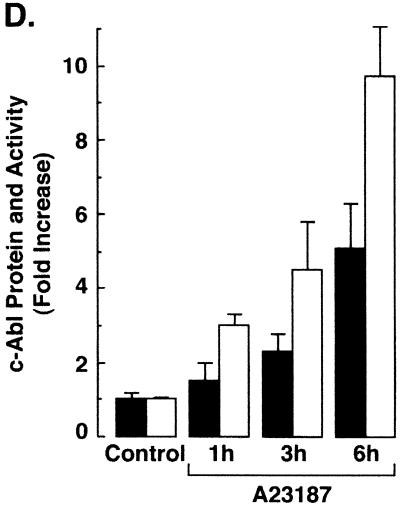
A23187 induces mitochondrial translocation of c-Abl. (A) Rat1 cells were treated with 10 μM A23187 and harvested at 6 h. Cytoplasmic and nuclear fractions were isolated and subjected to immunoblotting (IB) with anti-c-Abl, anti-β-actin, anti-PCNA, or anticalreticulin. (B) Rat1 cells were treated with 10 μM A23187 and harvested at the indicated times. Mitochondrial fractions were isolated and subjected to immunoblotting with anti-c-Abl or anti-HSP60. The signal intensities of c-Abl protein were compared to that of the control. (C) Rat1 cells were treated with 10 μM A23187 and harvested at the indicated times. Mitochondrial fractions were subjected to immunoprecipitation (IP) with anti-c-Abl. The precipitates were analyzed in a c-Abl kinase assay using GST-Crk(120–225) as the substrate or subjected to immunoblotting with anti-c-Abl. The signal intensities of c-Abl activity and protein were compared to that of the controls. (D) The increases in mitochondrial c-Abl protein (solid bars) and activity (open bars) are expressed as the means plus standard deviations obtained from three separate experiments.