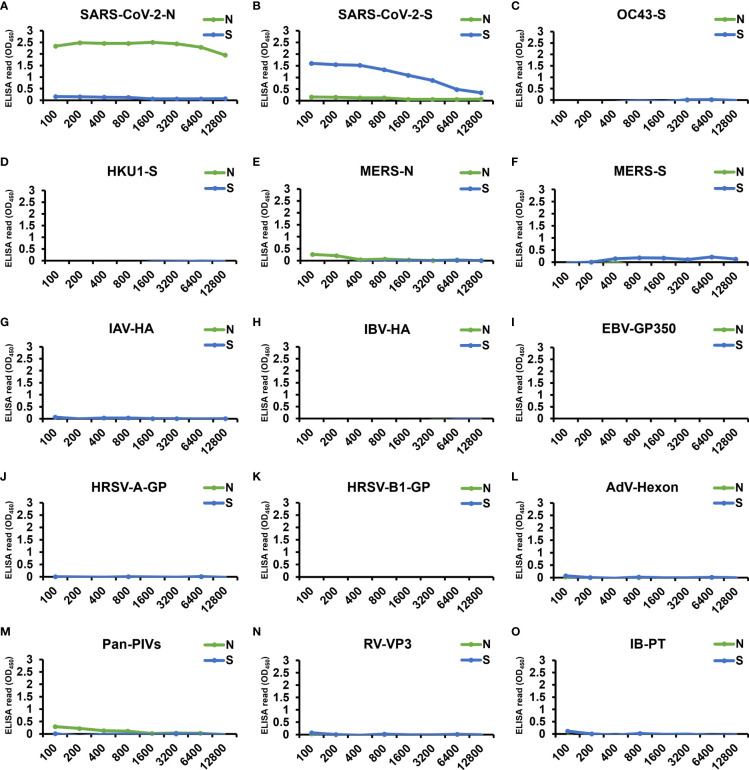
Figure 6.
Examination by our cell-based ELISAs of the cross-reactivity of antibodies from other human coronaviruses and viruses causing upper respiratory tract infection. The specificity of our cell-based ELISAs using N-cells (green) or S-cells (blue) was tested by applying 9 pAb, 5 mAb, and 1 patient serum. These include positive control antibodies, i.e., (A) SARS-CoV-2-N pAb and (B) SARS-CoV-2 S mAb, antibodies against other human coronavirus antigens, i.e., (C) OC43-S pAb, (D) HKU1-S pAb, (E) MERS-N pAb, and (F) MERS-S pAb, and antibodies specific to the antigen of viruses causing upper respiratory tract infections: (G) influenza A virus hemagglutinin (IAV-HA) pAb, (H) influenza B virus hemagglutinin (IBV-HA) pAb, (I) Epstein-Barr virus glycoprotein 350 (EBV-GP350) pAb, (J) human respiratory syncytial virus type A rsb1734 strain glycoprotein (HRSV-A-GP) pAb, (K) human respiratory syncytial virus B1 strain glycoprotein (HRSV-B1-GP) mAb, (L) adenovirus hexon protein (AdV-Hexon) mAb, (M) pan parainfluenza viruses (Pan-PIVs) mAb, and (N) rhinovirus outer capsid protein VP3 (RV-VP3) mAb. All antibodies were serially diluted from a starting concentration of 100 µg/mL. (O) A serum sample from an influenza B patient was also assessed (IB-PT). Each experiment was performed once. X-axes, antibody dilution factor.