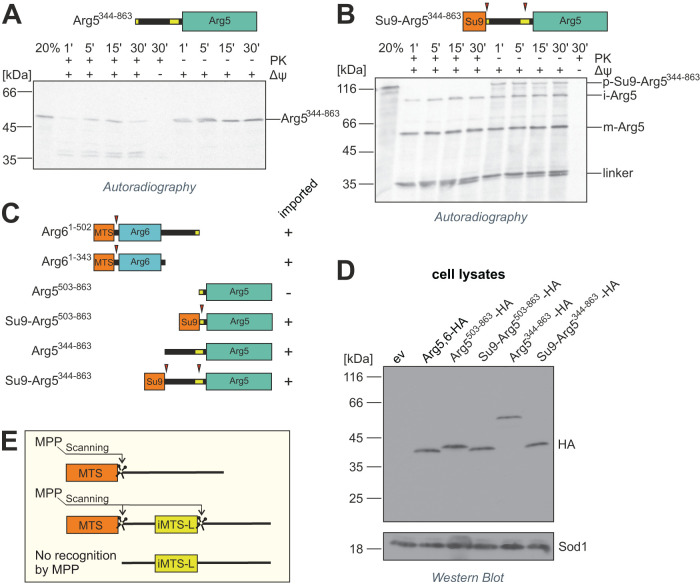
FIGURE 4:
MPP requires a strong N-terminal MTS for internal processing of precursor proteins. (A, B) Radiolabeled precursor proteins of Arg5344–862 and Su9-Arg5344–862 were incubated with isolated mitochondria for the indicated times and analyzed by SDS–PAGE and autoradiography. Nonimported material is digested with proteinase K (left half). Twenty percent of the total lysate used per import lane is loaded for control. The membrane potential (Δψ) was depleted with VAO. Red arrowheads indicate processing sites. p, precursor, i, intermediate, m, mature. (C) Overview of truncated Arg5,6 variants and their import competence. Su9, presequence of N. crassa subunit 9. (D) Yeast cells expressing indicated variants of Arg5,6, all carrying a C-terminal HA tag, were lysed and protein extracts were analyzed by SDS–PAGE and immunoblotting directed against the HA epitope or Sod1 as a loading control. ev, empty vector. (E) MPP cleaves the Arg5,6 precursors at its internal processing site only if they carry a bona fide N-terminal presequence. Presumably, MPP recognizes its substrates primarily at their N-terminus and then scans the downstream polypeptide for internal cleavage sites.