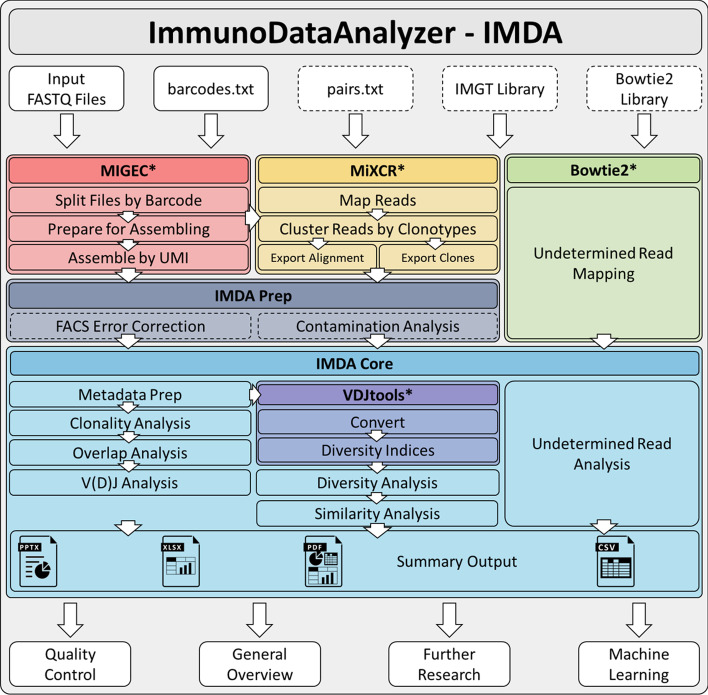
Fig. 1.
Schematic representation of the IMDA pipeline for automated processing of barcoded and unique molecular identifier (UMI) tagged immune repertoire NGS data starting with input files (compressed or non-compressed FASTQ files) and the barcode file (barcodes.txt). Optional files are represented in dashed white boxes. This includes the usage of different library files for better comparability and more efficient performance, e.g., the IMGT library used by MiXCR. Raw data pre-processing using open-source software tools such as MIGEC and MiXCR runs parallel to pre-processing of the undetermined reads. However, Undetermined Read Mapping and Analysis can only be performed if a Bowtie2 library file is provided. A FACS Error Correction module is implemented for cell subset disambiguation within the sub-process named IMDA Prep. If different cell types of one sample separated using FACS or magnetic sorting are sequenced, cell sorting errors can be reduced. The Contamination Analysis module enables the identification of shared UMIs within all samples as a measure of quality control in the case of cross-sample contamination. These two IMDA Prep modules are optional (dashed lines) and not mandatory required for IMDA Core analyses. The module IMDA Core provides methods for calculating clonality, diversity, clonotype overlap, sample similarity and V(D)J gene segment analysis, and undetermined read investigations. All data describing the dataset is summarized in a compact format, provides a general overview, enables first interpretations and quality control, and can be used as input for subsequent ML. * MIGEC, MiXCR, Bowtie2 and VDJtools are called and used as third-party tools