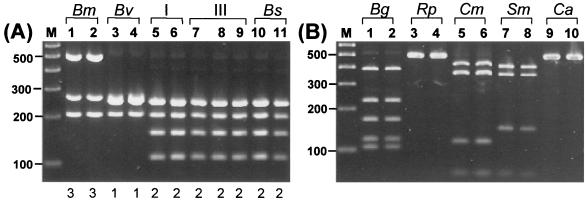
FIG. 1.
RFLP analysis of the 16S rRNA gene. (A) Analysis of the 16S rRNA gene of strains from the B. cepacia complex. Lanes: 1, LMG 13010T; 2, C1576; 3, LMG 10929T; 4, LMG 16232; 5, ATCC 25416; 6, ATCC 17759; 7, C5424; 8, C1394; 9, CEP511; 10, LMG 07000; and 11, LMG 14294. The genomovar status of each strain is indicated above the lane numbers, and the numerical 16S rRNA RFLP type is shown below each lane. Molecular size markers are shown in lane M (100-bp ladder). (B) Analysis of 16S rRNA genes of other bacterial species which may be misidentified as B. cepacia or grow on BCSA (10). Reference strains from Henry et al. (10): Lanes: 1, B. gladioli (Bg) CEP82; 2, B. gladioli CEP89; 3, R. picketti (Rp) ATCC 27511; 4, R. picketti ATCC 49129; 5, C. meningosepticum (Cm) FC113; 6, C. meningosepticum FC224; 7, S. maltophilia (Sm) CEP272; 8, S. maltophilia C4525; 9, C. acidovorans (Ca) FC77; 10, C. acidovorans CEP145. In panel A, the numerical 16S rRNA RFLP type of each isolate is shown below each lane.