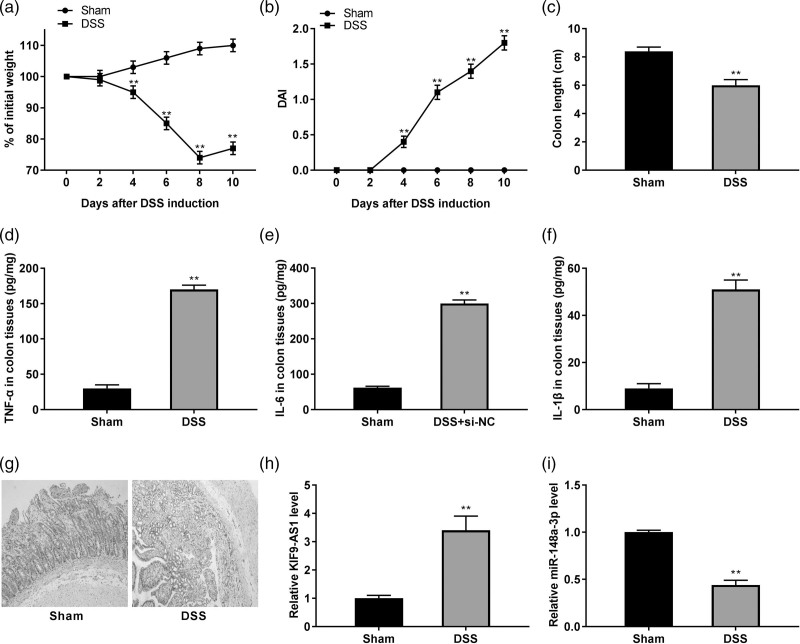
Fig. 2.
The colon injury and inflammation were enhanced in dextran sulfate sodium (DSS)-induced inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) model. (a) Bodyweight change in the sham group and the DSS group. **P < 0.01 vs. sham; (b) disease activity index (DAI) score of mice in the sham group and the DSS group. **P < 0.01 vs. sham; (c) colon length of mice in the sham group and the DSS group. **P < 0.01 vs. sham; (d–f) the concentrations of tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), interleukin (IL)-6, and IL-1β in colon tissues were determined by ELISA. **P < 0.01 vs. sham; (g) the histological injury of colon tissues was observed by hematoxylin-eosin (HE) staining; (h) quantitative real time PCR (qRT-PCR) was used to detect the expression of KIF9-AS1 in colon tissues. **P < 0.01 vs. sham; (i) the expression of miR-148a-3p in colon tissues was demonstrated using qRT-PCR. **P < 0.01 vs. sham.