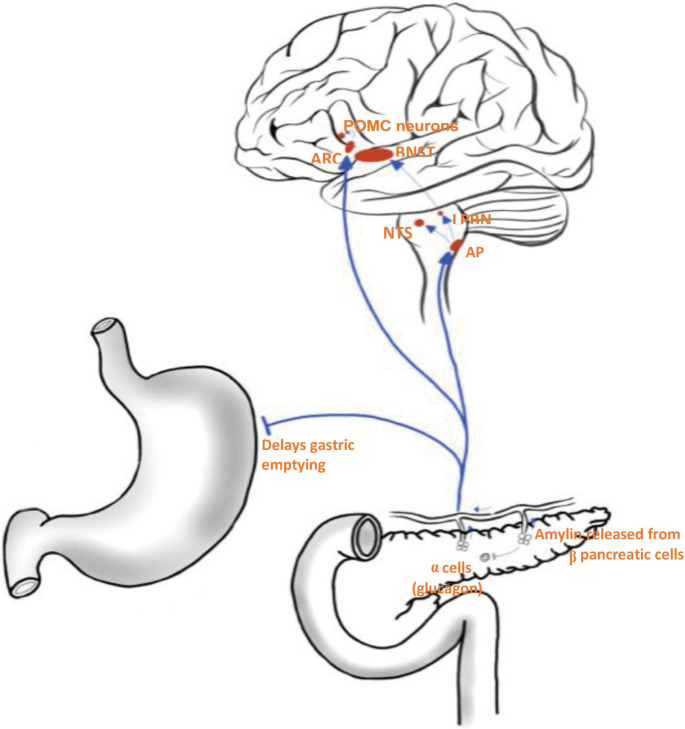
Figure 1.
Amylin functions as a satiety hormone. Released into the bloodstream by β pancreatic cells, amylin activates various homeostatic and reward centres in the brain to suppress appetite and reduce food intake. In addition, amylin acts as an inhibitory signal to delay gastric emptying and suppress the release of glucagon from α pancreatic cells. POMC, proopiomelanocortin; ARC, arcuate nucleus; BNST, bed nucleus of the stria terminalis; NTS, nucleus tractus solitarius; LPBN, lateral parabrachial nucleus; AP, area postrema.