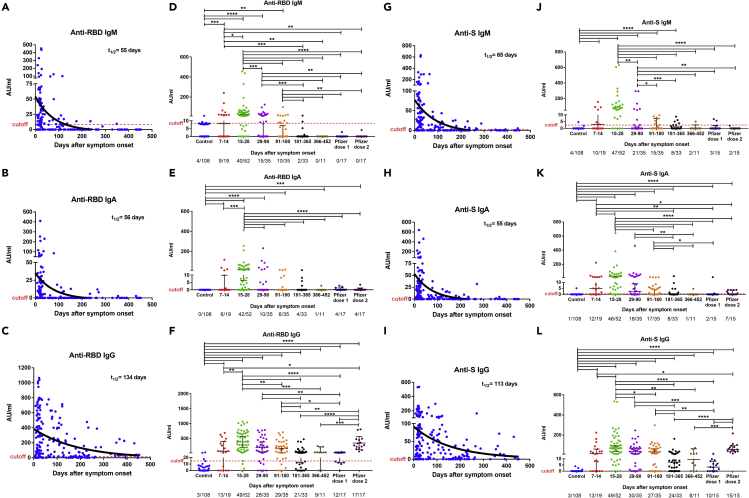
Figure 2.
Cross-sectional analysis of plasma anti-SARS-CoV-2 antibody titers patients over time
Levels of anti-RBD (A–F) and anti-S (G–L) IgM, IgA, and IgG antibodies in plasma of COVID-19 patients, historical controls, and vaccinated individuals. Antibodies were measured in 185 samples from 136 COVID-19 patients, 108 historical controls (before the SARS-CoV-2 pandemic), and 23 vaccinated individuals. The RBD (A–C) and S (G–I) specific IgM, IgG, IgA antibody decay curves (in black) and half-lives (t1/2) were estimated by a one-phase exponential decay model. Samples from patients were further divided in six study periods: 7–14 days (n = 19), 15–28 days (n = 52), 29–90 days (n = 35), 91–180 days (n = 35), 181–365 days (n = 33), and 366–452 (n = 11) after symptom onset (D–F and J–L) for comparison. Vaccinated individuals were sampled 14–35 days after the first dose and 14–36 days after the second dose. For each time interval, the proportion of positive samples is indicated below the X axis. Symbols represent individual subjects; horizontal black lines indicate the median and 95% CI. The dashed red line indicates the cutoff value for elevated anti-S and anti-RBD antibody titers (2.5 and 8.4 AU/mL for IgM, 0.5 and 0.08 AU/mL for IgA, and 0.03 and 14.81 AU/mL for IgG, respectively, giving a specificity of 96% for IgM, 99% for IgA, and 97% for IgG). The cutoff-value is not visible in some graphs because it is very close to the X axis. Mann-Whitney U test. ∗p ≤ 0.05, ∗∗p ≤ 0.01, ∗∗∗p ≤ 0.001, and ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001. See also Figures S1 and S2.