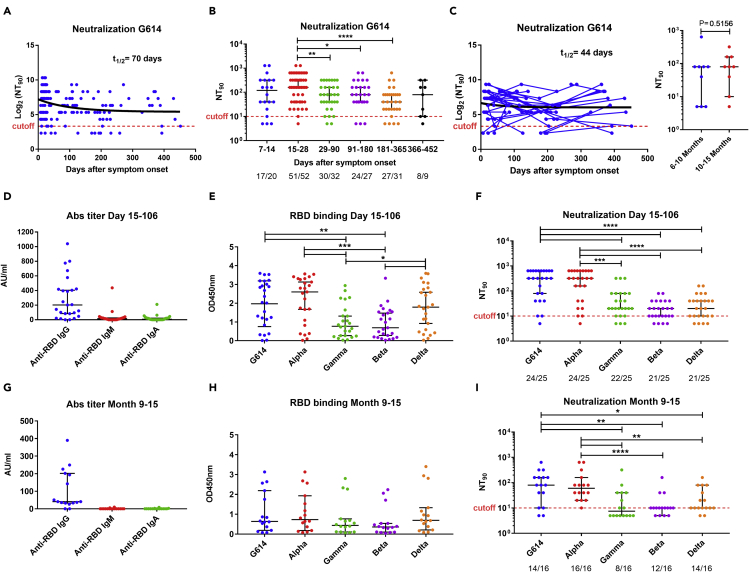
Figure 4.
Cross-sectional and longitudinal analysis of plasma neutralization activity against SARS-CoV-2 and variants of concern
(A) Dynamics of plasma neutralizing activity against G614 variant in COVID-19 patient samples over time.
(B) Samples from patients were taken at seven study periods: 7–14 days (n = 20), 15–28 days (n = 52), 29–90 days (n = 32), 91–180 days (n = 27), 181–365 days (n = 31), and 366–452 (n = 9) after symptom onset. For each time interval, the proportion of positive samples is indicated below the X axis.
(C) For longitudinal analysis, samples were taken at two (n = 31) or more (n = 7) time points and further comparisons were made between paired samples (n = 9) at two time points ranging from 6 to 15 months (TP1: 181–300 and TP2: 301–452 days after symptoms onset; right panel). The NT90 decay curves (in black) and corresponding half-lives (t1/2) were estimated by a one-phase decay model (A, C). To test cross-neutralization, the level of anti-RBD IgM, IgA, and IgG titers (D, G), binding activity of IgG antibody to RBD from SARS-CoV-2 variants (E, H), and plasma neutralizing activity against variants (F, I) were tested in plasma collected from COVID-19 patients at 15–106 days (median day of 24) and 9–15 months (241–452 days, median day of 370). The data in D and G represent a subset of data presented in Figure 2. The dashed red line indicates the titer cutoff value (≥1:10). The cutoff-value is not visible in some graphs because it is very close to the X axis. Symbols represent individual subjects; horizontal black lines indicate the median and 95% CI. Mann-Whitney U test. ∗p≤ 0.05, ∗∗p ≤ 0.01, ∗∗∗p ≤ 0.001, and ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001. See also Figures S1 and S2.