Figure 1. Example electrical image decomposition into axonal and somatic compartments along with biophysical theory.
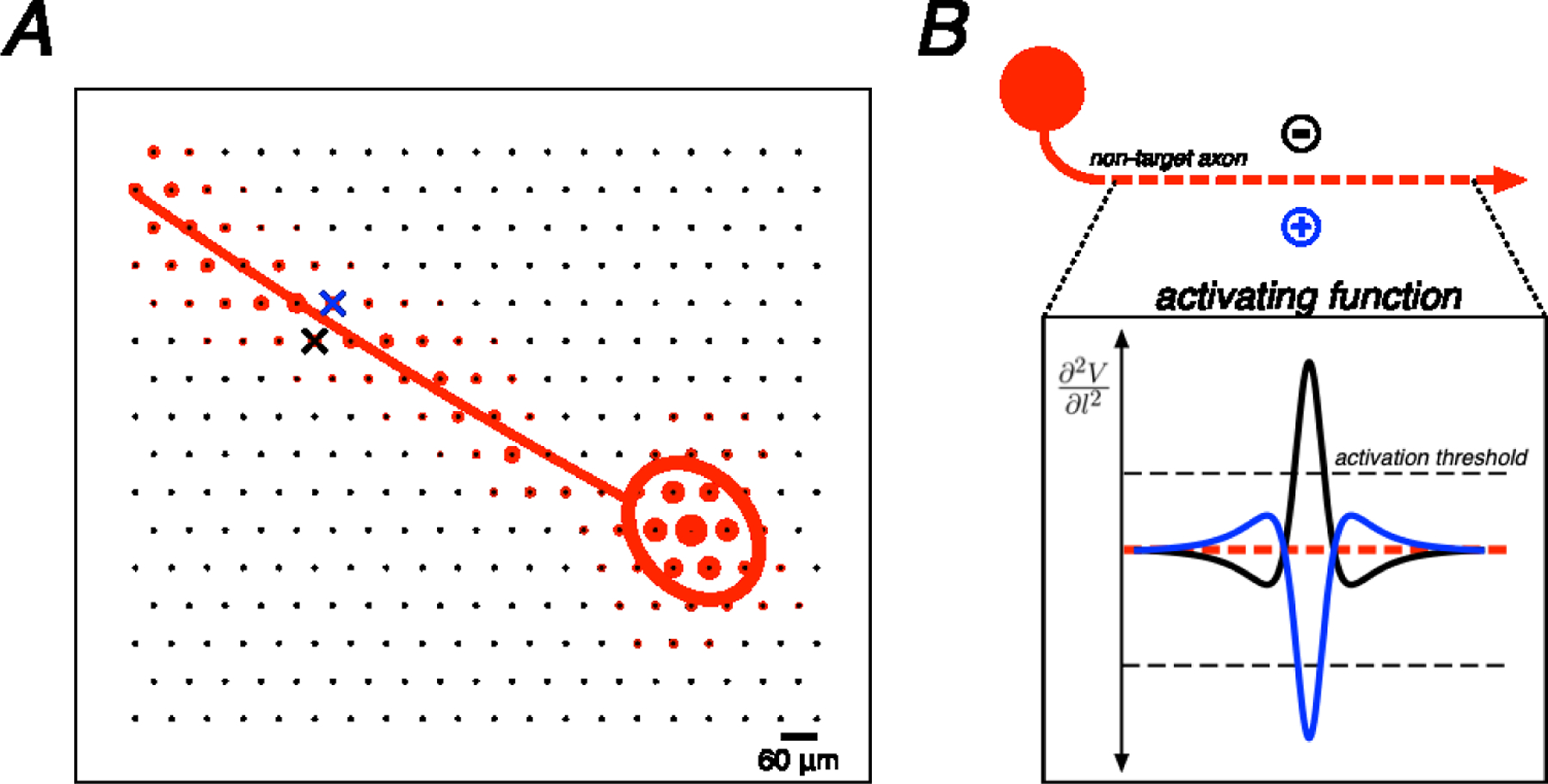
A. Spatial component of the electrical image for a single cell plotted on the electrode array along with polynomial axon trajectory fit and Gaussian somatic compartment fit. Crosses represent an example bi-electrode stimulation pattern, straddling the axon fit (blue cross, positive polarity electrode; black cross, negative polarity electrode). B. Example of an ideal bi-electrode stimulus: a pair of electrodes perfectly straddling an axon providing equal and opposite currents. The resulting activating function (the second spatial derivative of voltage along the length of the axon) from each active electrode is shown. Linear summation of electric fields implies that these activating functions would cancel perfectly in this idealized case.
