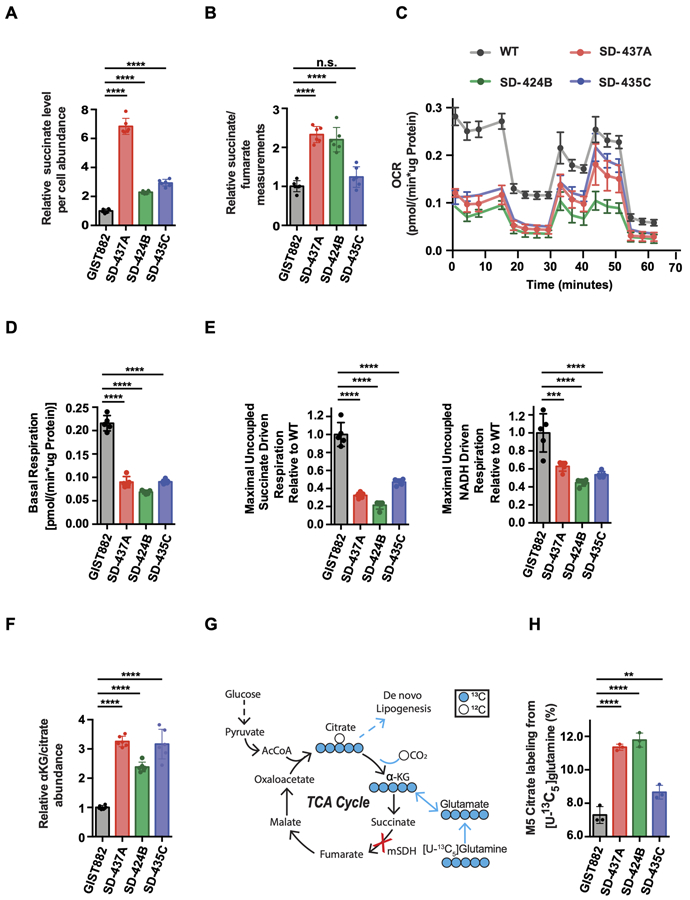
Figure 2. Metabolic profiles of mSDH GIST models recapitulate succinate dehydrogenase deficiency.
A. Per cell abundance of succinate relative to GIST882 in mSDH GIST models grown for 48 h (n = 3). One-way ANOVA (multiple comparisons) was performed for statistical analysis with ****, P<0.0001.
B. Ratio of intracellular succinate-to-fumarate concentrations relative to GIST882 in mSDH GIST models grown for 48 h (n = 3). One-way ANOVA (multiple comparisons) was performed for statistical analysis with P>0.05 (ns), ****, P<0.0001.
C. Oxygen consumption rate (OCR) trace of intact mSDH GIST models (n = 5).
D. Basal respiration rate of intact mSDH GIST models (n = 5). One-way ANOVA (multiple comparisons) was performed for statistical analysis with ****, P<0.0001.
E. Maximal uncoupled respiration driven by succinate relative to WT in permeabilized mSDH GIST models (n = 5). One-way ANOVA was performed. ***, P<0.001; ****, P<0.0001. Maximal uncoupled respiration driven by NADH relative to WT in permeabilized mSDH GIST models (n = 5). One-way ANOVA was performed. ***, P<0.001; ****, P<0.0001.
F. Ratio of intracellular α-ketoglutarate (α-KG) to citrate relative to GIST882 in mSDH GIST models grown for 48 h (n = 3).
G. Atom transition diagram of reductive glutamine catabolism using a [U-13C5] glutamine tracer. Open circles represent 12C, closed circles represent 13C carbon atoms.
H. Percent labeling of M5 citrate from [U-13C5]-glutamine in mSDH GIST models grown for 48 h (n = 3). Data are represented as mean ± SEM with biological replicates as indicated. One-way ANOVA was performed for statistical analysis with P>0.05 (ns), *, P<0.05; **, P<0.01; ***, P<0.001; ****, P<0.0001.