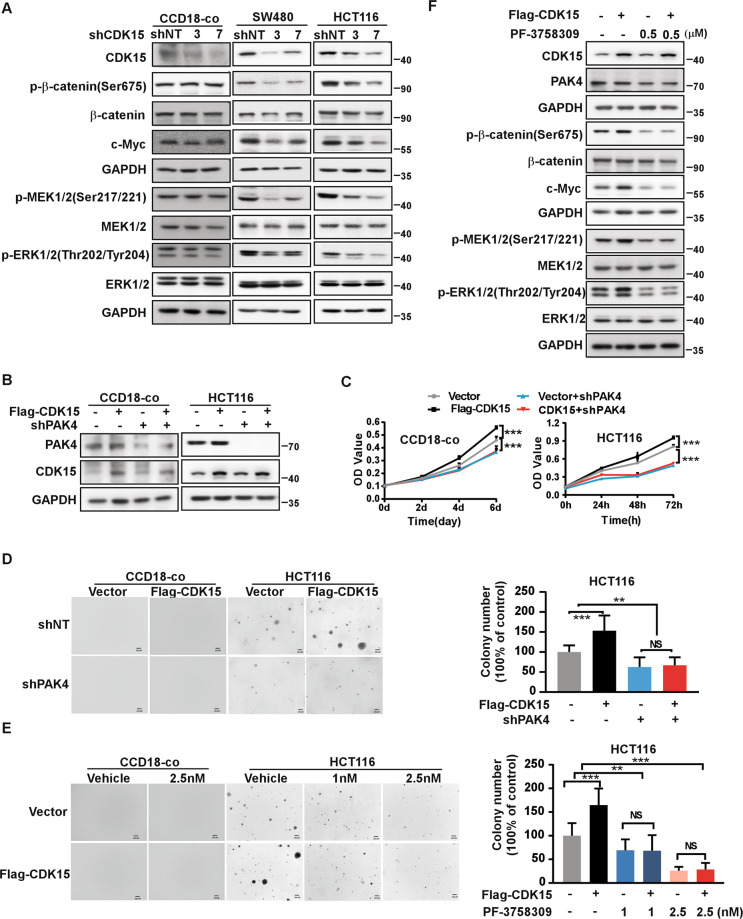
Fig. 5. PAK4 mediates the oncogenic effect of CDK15 in colorectal cancer.
A p-β-catenin(Ser675), c-Myc, p-MEK1/2 (Ser217/221), and p-ERK1/2 (Thr202/Tyr204) were detected by western blot after CDK15 knockdown in CCD18-co, SW480 and HCT116 cells. B Cells with PAK4 silencing and CDK15 overexpression were established. PAK4 and CDK15 expression was determined by western blot. C PAK4 knockdown reverses cell proliferation induced by CDK15 in CCD18-co and HCT116 cells. MTT assay was used to detect cell proliferation. D Anchorage-independent growth in CCD18-co and HCT116 cells with PAK4 silencing and CDK15 overexpression. Left panels: representative images (Scale bar: 200 μm). Right panels: Colonies were counted using Image J-Plus (Scale bar: 200 μm) and data represented statistical analysis of colony number ratio. E Anchorage-independent growth in CCD18-co and HCT116 cells treated with PAK4 inhibitor (PF-3758309). Left panel: representative images of colonies (Scale bar: 200 μm). Right panel: statistical analysis of the colony ratio. F Western blot to validate β-catenin and MEK/ERK signaling pathway in HCT116 cells with indicated treatment. Data were presented as mean values ± SD from triplicate experiments. Statistical differences were evaluated using Student’s t-test. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001.