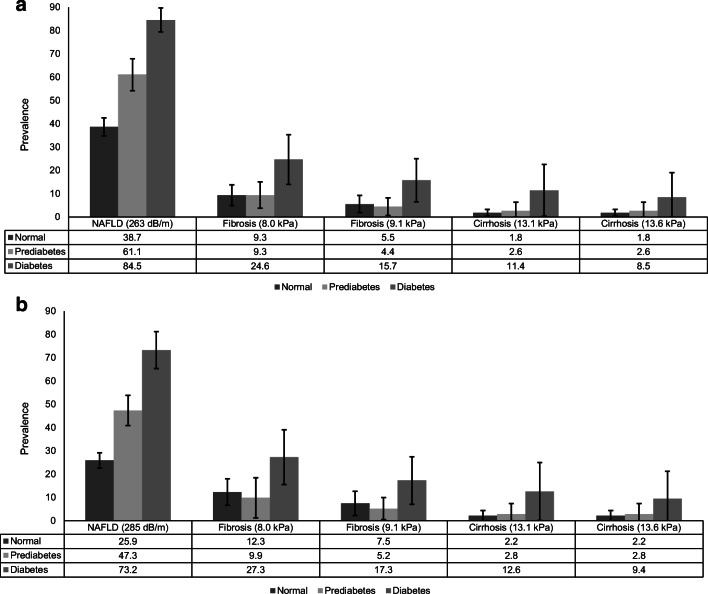
Figure 1.
Age-standardized prevalence of suspected nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and suspected fibrosis and cirrhosis by normal glucose tolerance, prediabetes, and diabetes in the USA, 2017–2018 (n=4,207). a Suspected NAFLD defined as controlled attenuation parameter (CAP) score ≥263 dB/m (cut-off values for 90% sensitivity) and suspected fibrosis (≥F2, liver stiffness measurement [LSM] ≥8.0 kPa or >9.1 kPa) and suspected cirrhosis (F4, liver stiffness measurement [LSM] ≥13.1 kPa or >13.6 kPa) among individuals with NAFLD. b Suspected NAFLD defined as controlled attenuation parameter (CAP) score ≥285 dB/m (cut-off values optimizing sensitivity and specificity) and suspected fibrosis (≥F2, liver stiffness measurement [LSM] ≥8.0 kPa or >9.1 kPa) and suspected cirrhosis (F4, liver stiffness measurement [LSM] ≥13.1 kPa or >13.6 kPa) among individuals with NAFLD.