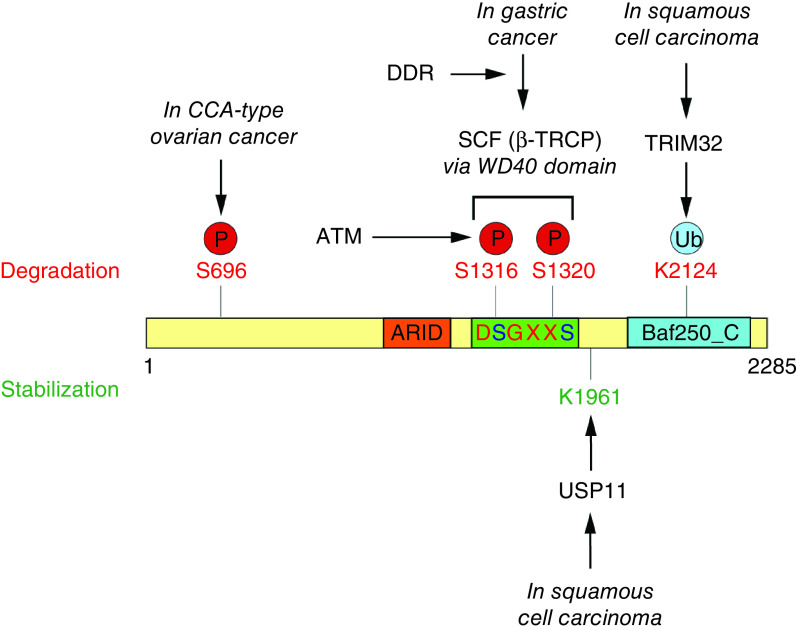
Figure 3. . Post-translational modification of the ARID1-containing protein in cancer.
In gastric cancer, DNA damage response signaling promotes phosphorylation of 1316 and 1320 serines in DSGXXS canonical degron site for β-TRCP recognition. Phosphorylation of Serines 1316 and 1320 requires ATM kinase activity. SCF (β-TRCP) interacts with phosphorylated recognition site via WD40 domain and results in proteasomal degradation of ARID1A. In squamous cell carcinoma, ARID1A is balanced by TRIM32 and USP11. TRIM32 ubiquitinates ARID1A at lysine 2124 to target for proteasomal degradation, while USP11 deubiquitinates ARID1A at lysine 1961 to stabilize the protein. In CCA-type ovarian cancer cell lines, p-Ser696-ARID1A levels is reduced compared with non-CCA cells possibly because of reduced phosphorylation or downregulation. Cancer-associated G2087R mutation induces ubiquitin-dependent proteasomal degradation of ARID1A.
CCA: Clear cell adenocarcinoma; SCF: Skp, Cullin, F-box containing complex.