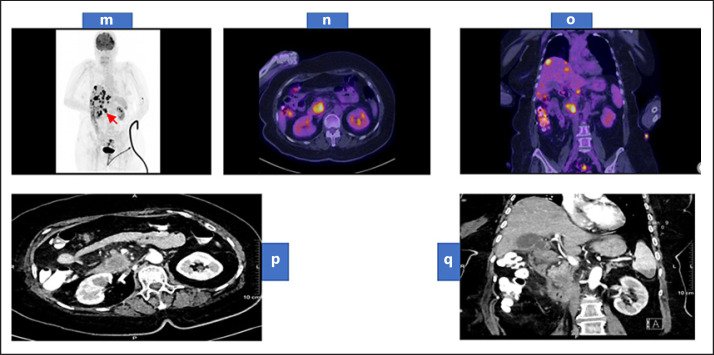
Fig. 3.
Whole-body maximum intensity projection of FDG PET scan (m) showing a hypermetabolic primary neoplasm at the pancreatic head (arrow) associated with multiple variable-sized hypermetabolic hepatic focal deposits and less avid lesion at the lower pole of the spleen. Trans-axial fused FDG PET/CT images of the abdomen (n) showing the hypermetabolic primary pancreatic head mass. Coronal fused FDG PET/CT images of the abdomen and pelvis (o) showing the hypermetabolic primary pancreatic head neoplasm associated with multiple hypermetabolic hepatic deposits. Contrast-enhanced CT of the abdomen arterial phase (p) axial view showing a large hypodense and hypovascular mass lesion arising from the pancreatic uncinated process. (q) coronal view showing multiple hypodense hepatic focal deposits and hypodense splenic focal lesion at its lower pole. PET, positron emission tomography; CT, computed tomography.