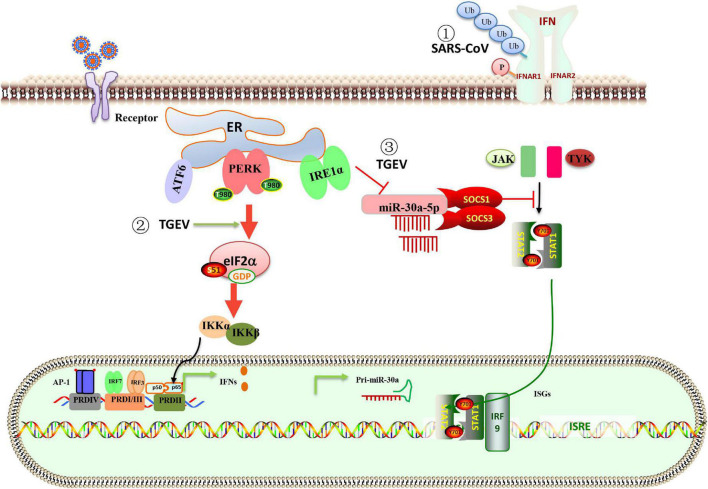
FIGURE 3.
Schematic representation of the interaction between ER stress, UPR, and innate immune system in response to coronavirus infection. (1) The PERK branch of UPR elicited by SARS-CoV 3a protein leads to ubiquitination, phosphorylation, and lysosomal degradation of IFNAR1 and inhibits IFN-I signaling. (2) TGEV infection activates the PERK-eIF2α pathway, the phosphorylation of eIF2α attenuates global protein synthesis, which decreases the levels of cytoplasm IκBα and leads to reduced inhibition of IκBα on NF-κB, promoting IFN-I production. (3) The IRE1 axis reduced host miR-30a-5p abundance, resulting in increased negative feedback regulators of JAK-STAT signaling, SOCS1 and SOCS3. High expression of SOCS1 or SOCS3 disrupted the antiviral effect of IFN-I. The data explain that TGEV evades the IFN-I antiviral response despite the intense induction of endogenous IFN-I.