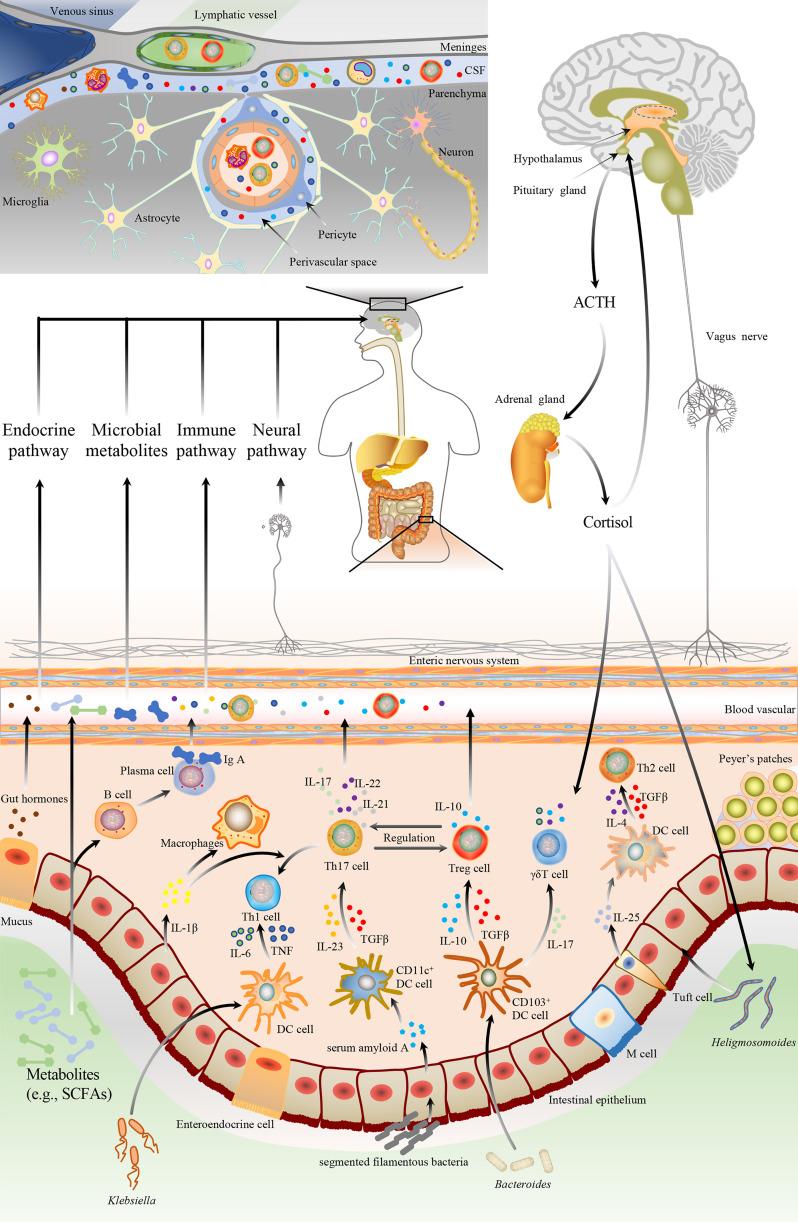
Figure 1.
The bidirectional communication pathways between the gut microbiota and brain. The gut microbiota could bi-directionally communicate with the brain through multiple pathways, including neuronal and non-neuronal. The brain regulates the gut microbiota via neuronal pathways (e.g., autonomic nervous system and enteric nervous system), hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis, etc. Neuronal pathways release neurotransmitters to modulate gut motility, gut barrier permeability, fluid maintenance, resident immune cell activation, and gut microbiota composition. HPA also releases cortisol to regulate gut homeostasis. Additionally, gut microbiota affects the development and pathophysiology of the brain by immunological, endocrine, metabolic, and neural pathways. Microbiomes and their metabolites could modulate the brain and behavior by affecting intestinal epithelial cells to alter gut barrier function, enteroendocrine cells to secret hormones, as well as dendritic cells and macrophage, to regulate immune and microglia activation. Gut microbiota can modulate the CD4+ T cells differentiation through epithelial cells or DC cells-mediated signals. ① Ectopic colonizing microbes, such as Klebsiella, can invade intestinal epithelium and stimulate DC cells to secrete proinflammatory cytokines, including IL-6 and TNF, which drive the polarization of Th1cells. ② SFB promotes Th17 polarization via epithelial cell-mediated CD11c+ DC cells activation. Epithelial cells release serum amyloid A to activate CD11c+ DC cells, leading to the TGF-β, IL-12, and IL-23 secretion. ③ Resident microbes, such as Bacteroides, modulate Treg cells generation by TGF-β and IL-10, which are secreted by CD103+ DC cells. CD103+ DC cells also can release IL-17 to promote γδT cell polarization. ④ Microbiota-associated Th2 cell polarization is correlated with parasite colonization such as Heligmosomoides, mediated by tuft cells secreting IL-25 to DC cells. Then activated DC cells release IL-4 and TGF-β to drive Th2 polarization. DC, dendritic cell; IL, interleukin; TNF, tumor necrosis factor; Th, T helper; TGF-β, transforming growth factor-β; SFB, segmented filamentous bacteria; SCFA, short-chain fatty acid; Treg, regulatory T cell.