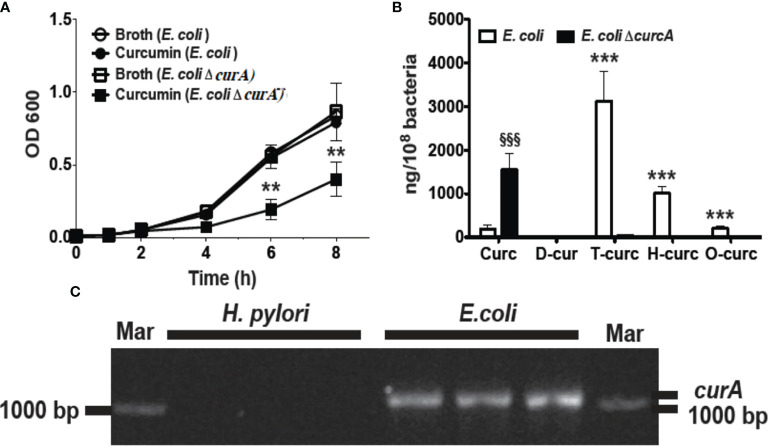
Figure 3.
Deletion of curA gene in E. coli results in growth inhibition by curcumin. (A) Growth curve of E. coli and its deletion mutant (ΔcurA) in the presence of curcumin or vehicle (**P value < 0.005 ***P value < 0.005). The deletion of curA was done by PCR splicing method in which a pair of primers flanking the region where the deletion to be made, two complementary primers comprising a region of -15 bp to +15 bp related to the junction point were used and a high fidelity polymerase was used for PCR. (B) Quantification of curcumin and its reduced metabolites dihydro-curcumin (D-curc), tetrahydro-curcumin (T-curc), hexahydro-curcumin (H-curc), and octahydro-curcumin (O-curc) in E. coli and its curA deletion mutant. (C) RT-PCR analysis of curA expression in genomic DNA isolated from H. pylori or E. coli. §§§P ≤ 0.001.