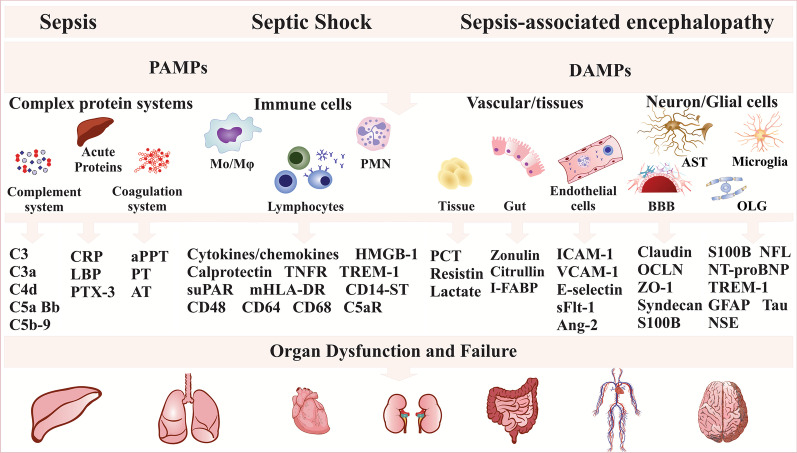
Fig. 1.
Sepsis, septic shock, and sepsis-associated encephalopathy biomarkers. The infection triggers a cascade of signaling pathways that activate several transcription factors and promote proinflammatory mediators such as acute-phase proteins, cytokines, chemokines, and antimicrobial peptides necessary to eliminate the invading pathogens. The unbalanced host immune response triggers vascular endothelial damage, increasing gut and BBB permeability, culminating in organ dysfunction. Ang-2 (angiopoietin-2), APP (acute phase proteins), aPPT (activated partial thromboplastin), AST (astrocytes), AT (antithrombin), BBB (blood–brain barrier), C5aR (complement component 5a receptor), CD (cluster of differentiation), CD14-ST (soluble subtype of CD14), CRP (C reactive protein), DAMPs (damage-associated molecular patterns), GFAP (glial fibrillary acidic protein), HMGB-1 (high mobility group box 1), ICAM-1 (intercellular adhesion molecule 1), I-FABP (intestinal fatty acid binding protein), LBP (lipopolysaccharide binding protein), mHLA-DR (monocytic human leukocyte antigen DR), Mo (macrophage), NFL (neurofilament light), NSE (neuron specific enolase), NT-proBNP (N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide), OCLN (occludin), OLG (oligodendrocyte), PAMPs (pathogen-associated molecular patterns), PCT (procalcitonin), PMNL (polymorphonuclear leukocytes), PT (prothrombin), PTX-3 (pentraxin-3), S100B (calcium-binding protein B), sFlt-1 (soluble fms-like tyrosine kinase 1), suPAR (soluble form of the urokinase plasminogen activator receptor), TNFR (tumor necrosis factor receptor type), TREM-1 (triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells 1), VCAM-1 (vascular cell adhesion molecule 1), ZO-1 (zonula-occluden 1)