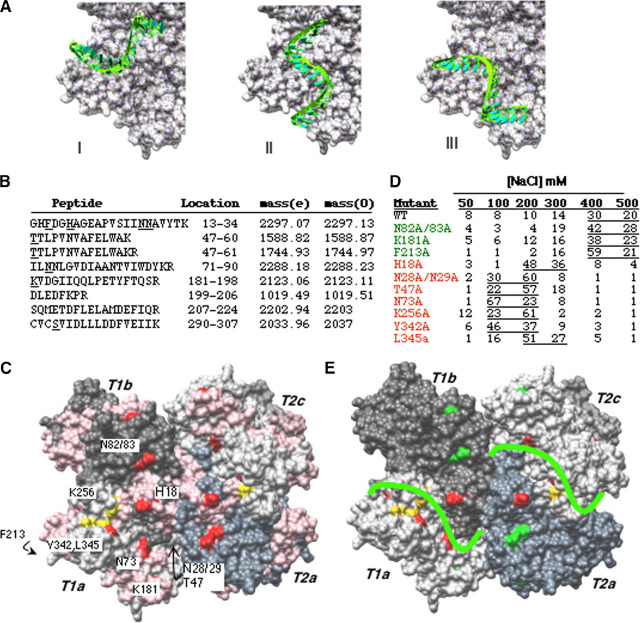
FIGURE 5.
A Model for a complex between Nsp15 and oligonucleotide RNA.A, putative RNA binding path of sNsp15 hexamer. For clarity, only subunit T1A is emphasized. A U16 A-RNA oligonucleotide is manually docked through the narrow catalytic site of the enzyme. B, summary of Nsp15 peptides obtained by biotin-streptavidin affinity chromatography and reversible cross-linking and trypsin digestion. The peptides were purified using Zip-tip as recommended by the manufacturer and subjected to MALDI-ToF. The expected masses obtained by virtual tryptic digestion of Nsp15 are denoted by (e) and the masses of observed peptide peaks from MALDI-ToF analysis are denoted by (0). The peptide position on the protein sequence is indicated by protein sequence as well as residue numbers. C, location of peptides identified by reversible RNA cross-linking and MALDI-ToF analysis. Identified peptides are colored pink. Potential RNA binding residues, along trajectories selected for mutational analysis are colored red. Active site residues are colored by element. D, affinity chromatography analysis of Nsp15 mutant and wild type proteins. All of the proteins were allowed to bind to polyU-agarose at 30 mm sodium chloride concentration followed by washing the slurry with sodium chloride concentrations indicated on top. Protein in each fraction was quantified by the Coomassie Plus protein assay kit from Pierce and is indicated as a percentage of the amount loaded. E, favored RNA binding path on Nsp15. Color scheme is as follows: protein subunits, shades of gray; active site residues, yellow; residues that affected affinity of protein for RNA, red; residues that did not affect RNA binding, green. A green line indicating RNA path is drawn on protein surface.