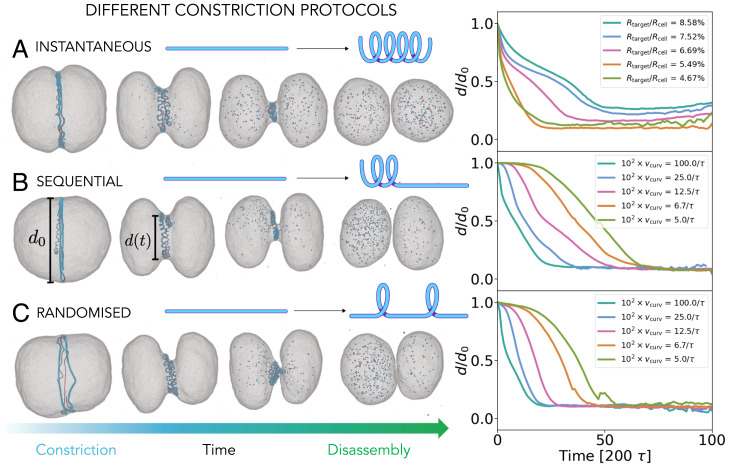
Fig. 4.
Different protocols for the curvature change. (A) Instantaneous: The target filament radius changes globally throughout the filament to , as indicated in the key, within a single time step. (B) Sequential: The filament curvature change starts at one end of the filament and propagates at a rate to the other end, here shown for . (C) Randomized: Random bonds along the filament constrict at a rate , here shown for . In all the protocols, once the entire filament has transitioned, it is disassembled from both ends at a rate . The value of does not influence the division curves (SI Appendix, Fig. S4). A–C, Right compare the normalized diameter of the cell at the midzone as a function of time. We selected only simulations that led to division and averaged over simulation seeds and different disassembly rates.