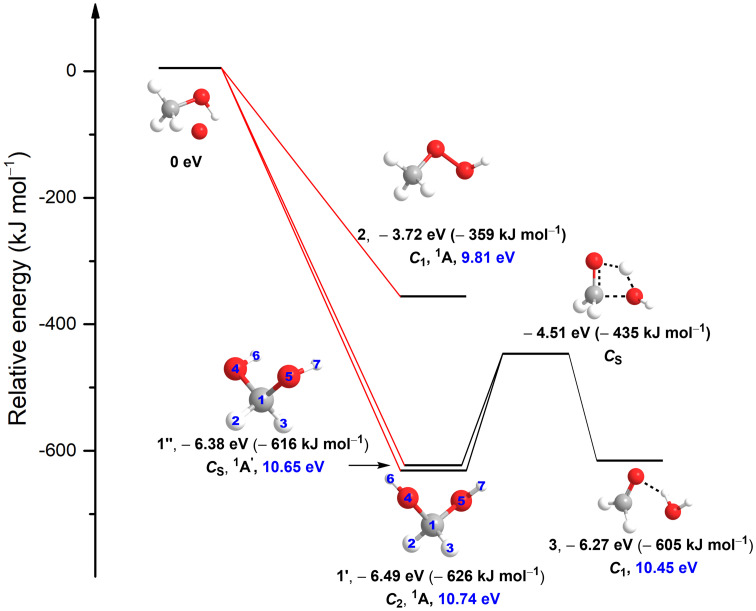
Fig. 1.
Molecular structures of CH4O2 isomers. Relative energies, point groups, electronic ground states, and adiabatic ionization energies (blue) of CH4O2 isomers are also compiled. The energies were computed at the coupled cluster singles, doubles, and perturbative triples level with a complete basis set extrapolation [CCSD(T)/CBS] and include zero-point vibrational energy corrections. The atoms are color coded in gray (carbon), white (hydrogen), and red (oxygen). The formation of methanediol [(CH2(OH)2], 1’ and 1’’) and methyl peroxide (CH3OOH, 2) via excited-state oxygen atom [O(1D)] insertion into a carbon–hydrogen and carbon–oxygen/oxygen–hydrogen bonds of methanol (CH3OH), respectively, are barrierless. The transition state of the decomposition of methanediol [(CH2(OH)2], 1’ and 1’’) to a formaldehyde (H2CO) and water (H2O) complex (H2CO···H2O, 3) is also shown.