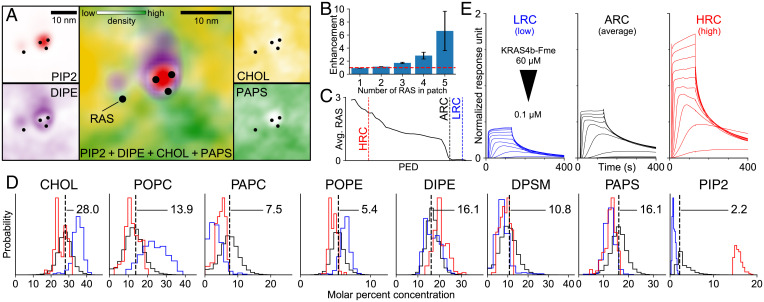
Fig. 2.
Lipid-dependence of RAS colocalization. (A) Representative macro model inner leaflet lipid densities around RAS, shown separately (small boxes) and together (large central box). Color saturation indicates local lipid density. (B) Population ratio of RAS multimer sizes observed in the macro simulation vs. a random uniform distribution. (C) Average number of RAS in macro model regions (radius 5 nm) along the primary embedding dimension (PED) from function preserving projection analysis (SI Appendix, S2.8.2). Vertical lines denote thresholds used to define high-RAS (HRC), initial average (ARC), and low-RAS (LRC) lipid compositions. (D) Distributions of inner leaflet lipid concentrations for all patches with RAS (black), HRC (red), and LRC (blue). The ARC is represented by a dashed vertical line. (E) Surface plasmon resonance sensorgrams of RAS adhesion to liposomes with the LRC, ARC, and HRC lipid compositions. Each subplot contains multiple traces representing distinct RAS concentrations (twofold dilutions, 60 to 0.1 μM).