FIG. 1 |. A unique set of mediators informs the communication between cancer stem cells and innate immune cell populations.
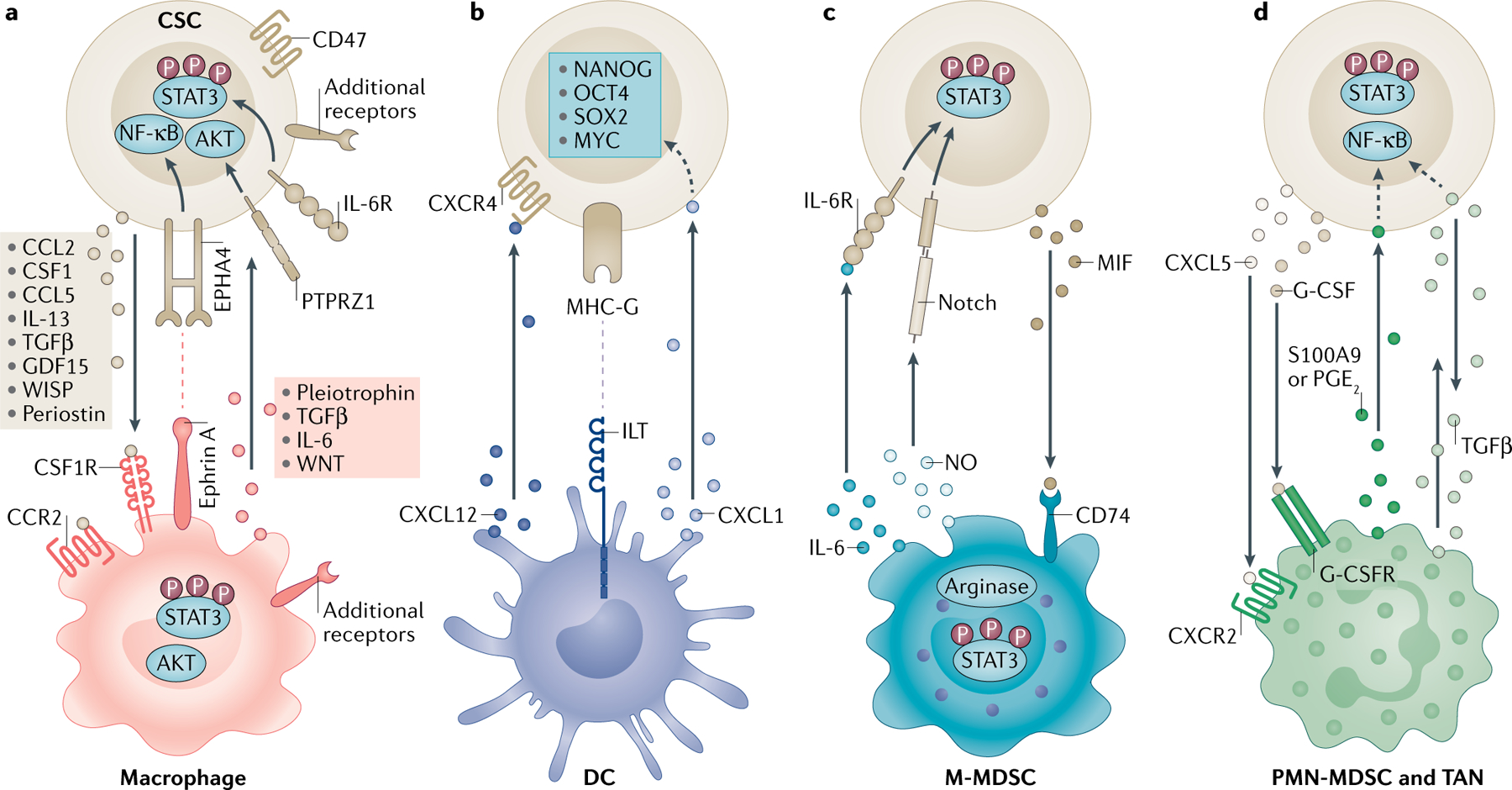
Reciprocal communication between cancer stem cells (CSCs) and myeloid cells through soluble mediators or juxtacrine signalling promotes immunosuppression and stemness. a | CSCs drive monocytes and macrophages via molecules including C-C motif chemokine 2 (CCL2), CCL5, colony-stimulating factor 1 (CSF1), transforming growth factor-β (TGFβ), growth/differentiation factor 15 (GDF15), WNT-induced signalling protein 1 (WISP1) and periostin that bind to surface receptors, including CSF1 receptor (CSF1R) and C-C chemokine receptor type 2 (CCR2). Macrophages, in return, express factors including interleukin-6 (IL-6), IL-13, pleiotrophin and TGFβ that signal through receptors such as receptor-type tyrosine-protein phosphatase-ζ (PTPRZ1) and ephrin type A receptor 4 (EPHA4) to support CSCs. These interactions activate the downstream signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3), AKT and nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) pathways. CSCs also evade macrophage phagocytosis through CD47 expression. b | CSCs interfere with dendritic cell (DC) maturation through major histocompatibility complex class I antigen G (MHC-G)–immunoglobulin-like transcript (ILT) inhibitory receptor interaction. Tolerogenic DCs release C-X-C motif chemokine 12 (CXCL12), which serves as a ligand to C-X-C chemokine receptor type 4 (CXCR4) and CXCL1 to promote CSCs. These interactions lead to the activation of the stem cell transcription factors NANOG, OCT4, SOX2 and MYC. c | Nitric oxide (NO) produced by monocytic myeloid-derived suppressor cells (M-MDSCs) activates Notch on CSCs, and IL-6 signalling increases STAT3 phosphorylation. CSCs recruit M-MDSCs via macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF) through CD74. CSCs also promote arginase 1 and STAT3 signalling in M-MDSCs. d | The CXCL5–CXCR2 axis and granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF) recruit tumour-associated neutrophils (TANs) and polymorphonuclear MDSCs (PMN-MDSCs). In return, prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) and S100A9 support stemness. TGFβ has a bidirectional role in this communication axis. Dashed arrows indicate indirect associations. G-CSFR, granulocyte colony-stimulating factor receptor; IL-6R, interleukin-6 receptor.
