Figure 1.
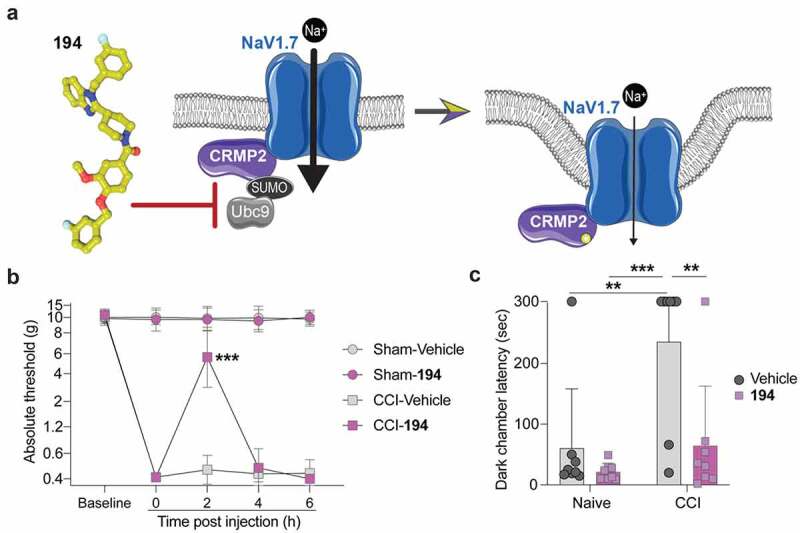
Compound 194 inhibits evoked and affective pain in rats with chronic constriction injury (CCI). (a) Schematic of the mode of action of compound 194 which uncouples the interaction between CRMP2 and the E2 SUMO-conjugating enzyme Ubc9 to prevent CRMP2 SUMOylation and reduces NaV1.7 cell-surface localization. This reduces sodium currents to alleviate pain. Image generated with BioRender. (b) Mechanical withdrawal thresholds were assessed in adult male rats before injury to establish a baseline and following injury to demonstrate the development of mechanical allodynia. Rats were then orally administered compound 194, which reversed mechanical allodynia in the CCI group (pink squares) compared to the CCI animals given the vehicle (gray squares) (CCI-Vehicle vs. CCI-194, p = 0.0001 at 2 hours post injection). This effect peaked at 2 hours post administration before the animals returned to their postsurgery baseline sensitivity level. (c) Nociception was evaluated using the operator-independent mechanical conflict-avoidance assay. Naïve rats treated with 194 (pink squares) had the same latency to cross an aversive sharp surface as their vehicle treated counterparts (gray circles). Animals that had neuropathic pain induced by CCI had a profoundly increased latency to cross the aversive surface to escape the brightly lit enclosure (gray circles, right). Treatment with 194 significantly reduced the time to cross the aversive surface (pink squares, right) indicating reduced mechanical allodynia. (For B, multiple Mann–Whitney tests, n = 8 per group; for C, two-way ANOVA, naïve vehicle vs CCI vehicle, p = 0.0036; naïve 194 vs CCI vehicle, p = 0.0004; CCI vehicle vs CCI 194, p = 0.0045, n = 8 per group).
