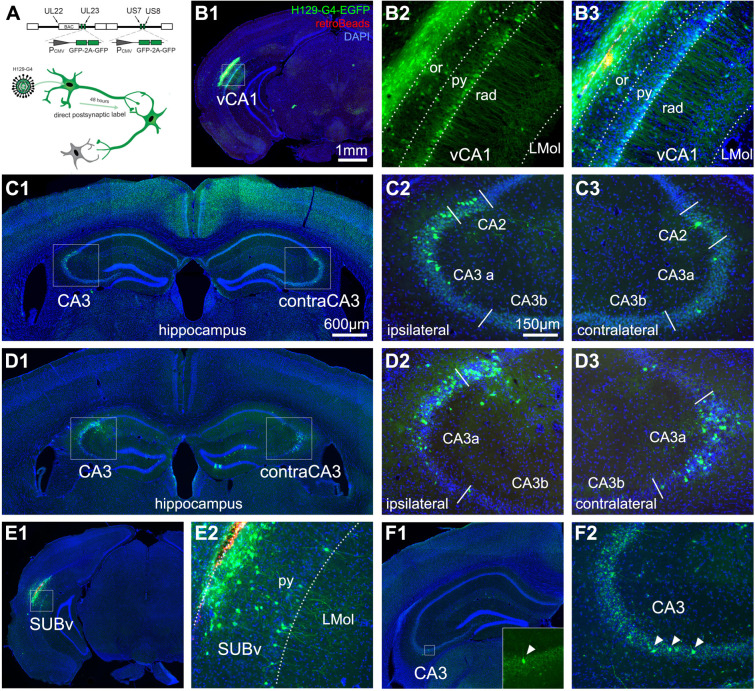
Fig 6. Anterograde HSV (H129 strain) tracing verifies direct projections from vCA1 and SUB to dCA3.
(A) Schematic for anterograde H129-G4 for time-limited mapping of direct monosynaptic projections. Top: Illustration of the genetically modified H129-based viral vector with the insertion of 4 copies of EGFP (2 tandem EGFP cassettes) into the H129 genome. Bottom: Empirically determined timeline of propagation of H129-G4 for anterograde monosynaptic tracing. (B) Representative section images of the vCA1 injection site with H129-G4. B1: The H129-G4 injection site labeling (green = GFP, red = Retrobeads microspheres, blue = DAPI throughout all panels). B2: The EGFP-labeled neurons in the pyramidal layer (py) and oriens layer (or) of vCA1. B3: The merged image of H129-G4 expression and red microspheres that were co-injected with the H129 virus. (C) Representative section images for H129-G4 tracing from vCA1. C1: H129-G4 labeled neurons in dCA3 of both hemispheres. Enlarged views of the boxed regions in C1 are shown in C2 and C3. (D) Examples from a different case show H129-G4 tracing from vCA1. (E, F) Representative sections for H129-G4 tracing from SUBv. E1. The H129-G4 virus injection site. E2 shows the EGFP-labeled neurons in the py of SUBv. F1. H129-G4 labeled neurons in dCA3. An enlarged view of the boxed region in F1 is shown in the bottom right corner. F2. Verification of the noncanonical input by a different case of H129-G4 tracing from SUBv. The scale bar (1 mm) applies to B1 and E1; the scale bar (600 μm) applies to C1, D1, and F1; and the scale bar (150 μm) applies to B2, B3, C2, C3, D2, D3, E2, and F2. dCA3, dorsal CA3; HSV, herpes simplex virus.